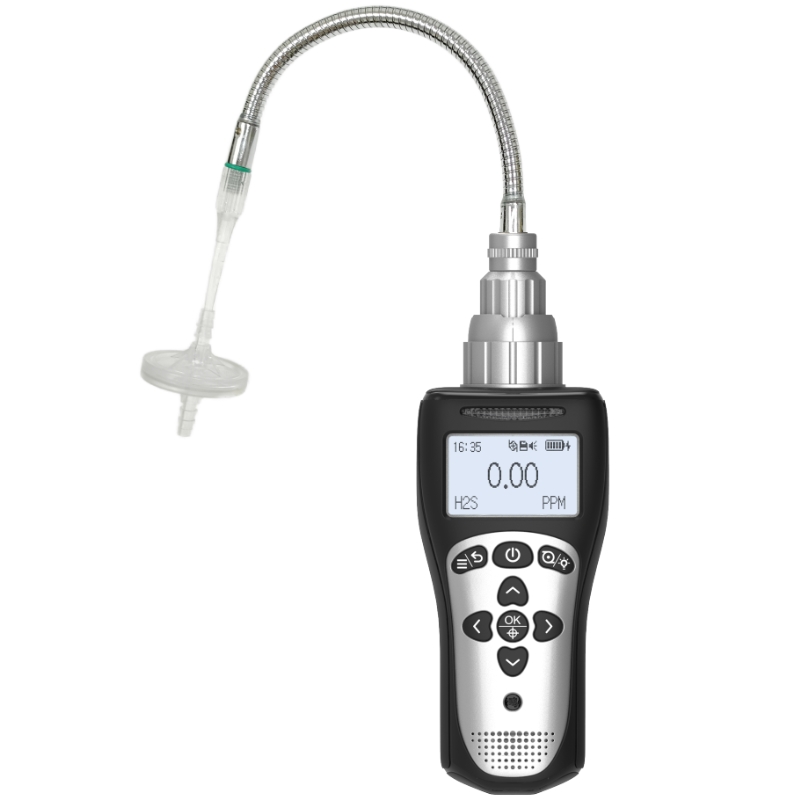
How to Maintain Your Oxygen Detectors for Optimal Performance?
In various industrial, scientific research, and outdoor adventure scenarios, oxygen detectors are critical devices for ensuring safety and smooth operations. For international users, understanding and mastering proper maintenance methods can keep oxygen detectors performing at their best, providing reliable support for all activities.

Regular Calibration: The Foundation of Accurate Detection
Regular calibration is the core component of oxygen detector maintenance. Since sensors may drift over time, leading to inaccurate detection data, calibration must be performed at the intervals recommended by the manufacturer. Generally, new devices should be calibrated before their first use and after each prolonged period of storage. For frequently used instruments, monthly calibration is appropriate; for less frequently used instruments, calibration every three months is sufficient.
Calibration requires the use of standard gases, ensuring that gas concentrations are accurate and within their validity period. During the process, first place the instrument in clean air to zero it, then connect it to the standard gas source, and adjust the display value to match the standard gas concentration according to the instrument manual. This process must be strictly followed to avoid calibration errors caused by operational mistakes. After calibration, record the calibration date and results for future tracking and management.
Sensor maintenance: The key to oxygen detection
The sensor is the “heart” of the oxygen detector, and its performance directly affects the accuracy of the detection results. Maintenance methods vary slightly depending on the type of sensor. Electrochemical sensors are sensitive to humidity and temperature, so they should be avoided exposure to extreme environmental conditions. If the instrument is not used for an extended period, the sensor can be removed from the instrument, stored in a sealed bag, and accompanied by desiccant to prevent moisture damage.
For optical sensors, the optical window should be cleaned regularly. Use a clean, soft, lint-free cloth to gently wipe away dust and stains, ensuring that light can pass through normally. Avoid touching the optical window to prevent fingerprints or scratches that may affect the sensor's sensitivity.
Cleaning and Dust Prevention: Keeping the Instrument Clean
Regularly cleaning the outer casing and internal components of the oxygen detector can effectively prevent the accumulation of dust and dirt, ensuring the instrument operates normally. When cleaning the outer casing, use a slightly damp soft cloth to gently wipe it down. Avoid using cleaning agents containing corrosive chemicals, as they may damage the surface of the casing. For dust inside the instrument, use a compressed air canister to gently blow it away, but be careful not to damage the internal electronic components.
After using the instrument in a dusty environment, clean it promptly. Additionally, equipping the instrument with a dust cover or storing it in a dust-proof box can reduce the chance of dust entering and extend the instrument's service life.
Battery Management: Providing Long-Lasting Power
The battery is the power source for the oxygen detector, and proper battery management is critical. Use original batteries or batteries that meet the manufacturer's specifications, and avoid using low-quality batteries that may cause instrument damage or performance degradation. Regularly check the battery level, and replace the battery promptly when the level drops below a certain threshold to avoid affecting normal instrument operation.
When the instrument is not in use for an extended period, remove the battery to prevent leakage and corrosion of the internal circuitry. Store the battery in a dry, cool place to avoid high temperatures and humidity, which can affect battery performance.
Proper Storage: Protecting Instrument Safety
Proper storage protects the oxygen detector from damage. Store the instrument in a dry, well-ventilated area, away from direct sunlight and high temperatures. Excessive heat may cause sensor performance degradation or even damage the instrument. Additionally, keep the instrument away from strong magnetic fields and corrosive gases to prevent interference or corrosion of internal electronic components.
In summary, by regularly calibrating the instrument, maintaining the sensor with care, keeping it clean, managing the batteries properly, and storing it safely, users can ensure the oxygen detector remains in optimal condition, providing a reliable safeguard for both safety and operational quality.
Related information
-

How to Calibrate an Oxygen Detectors to Ensure Accuracy?
In fields such as industrial safety, confined space operations, environmental monitoring, and even medical support, the measuremen...
2026-01-14 -

What is the measurement range of an oxygen detectors?
Oxygen detectors are indispensable equipment in industrial safety, environmental monitoring, and confined space operations. Accura...
2026-01-13 -

What is the normal oxygen concentration for an oxygen detectors?
Oxygen (O₂) is a vital gas for sustaining human life and most combustion processes. However, both excessively high and low oxygen...
2026-01-12 -

How Do Nitrogen Oxide Detectors Work?
Against a backdrop of growing global concern over air quality and emissions compliance, the precise monitoring of nitrogen oxides ...
2026-01-09 -

Operating Instructions for Nitrogen Oxide Detectors
Nitrogen oxides (NOₓ, primarily comprising nitrogen monoxide NO and nitrogen dioxide NO₂) are significant atmospheric pollutants...
2026-01-07











 info@eranntexgas.com
info@eranntexgas.com

 13480931872
13480931872