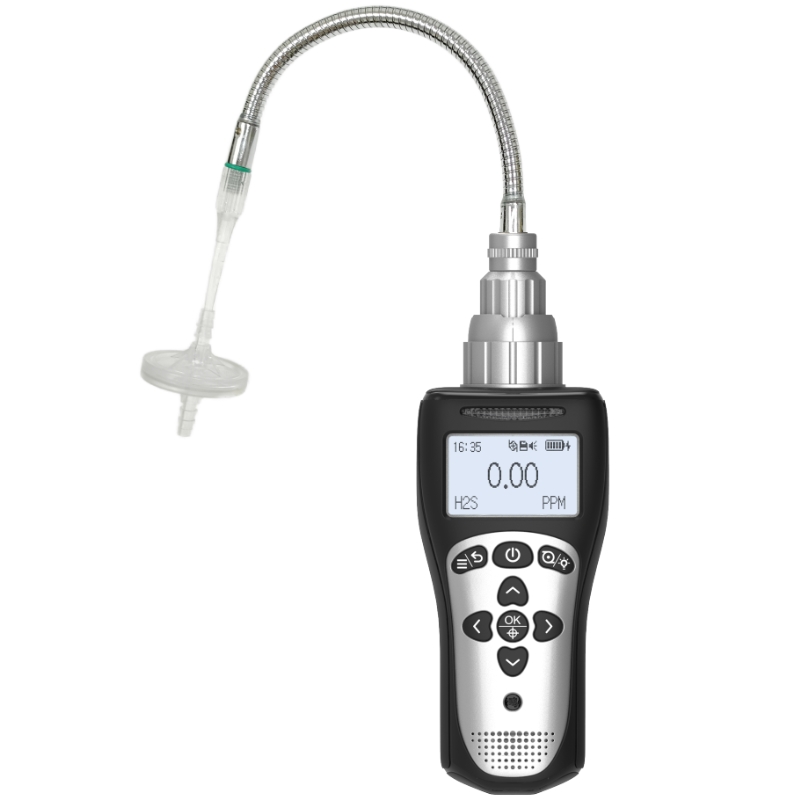
What Should You Know About 4-in-1 Detectors?
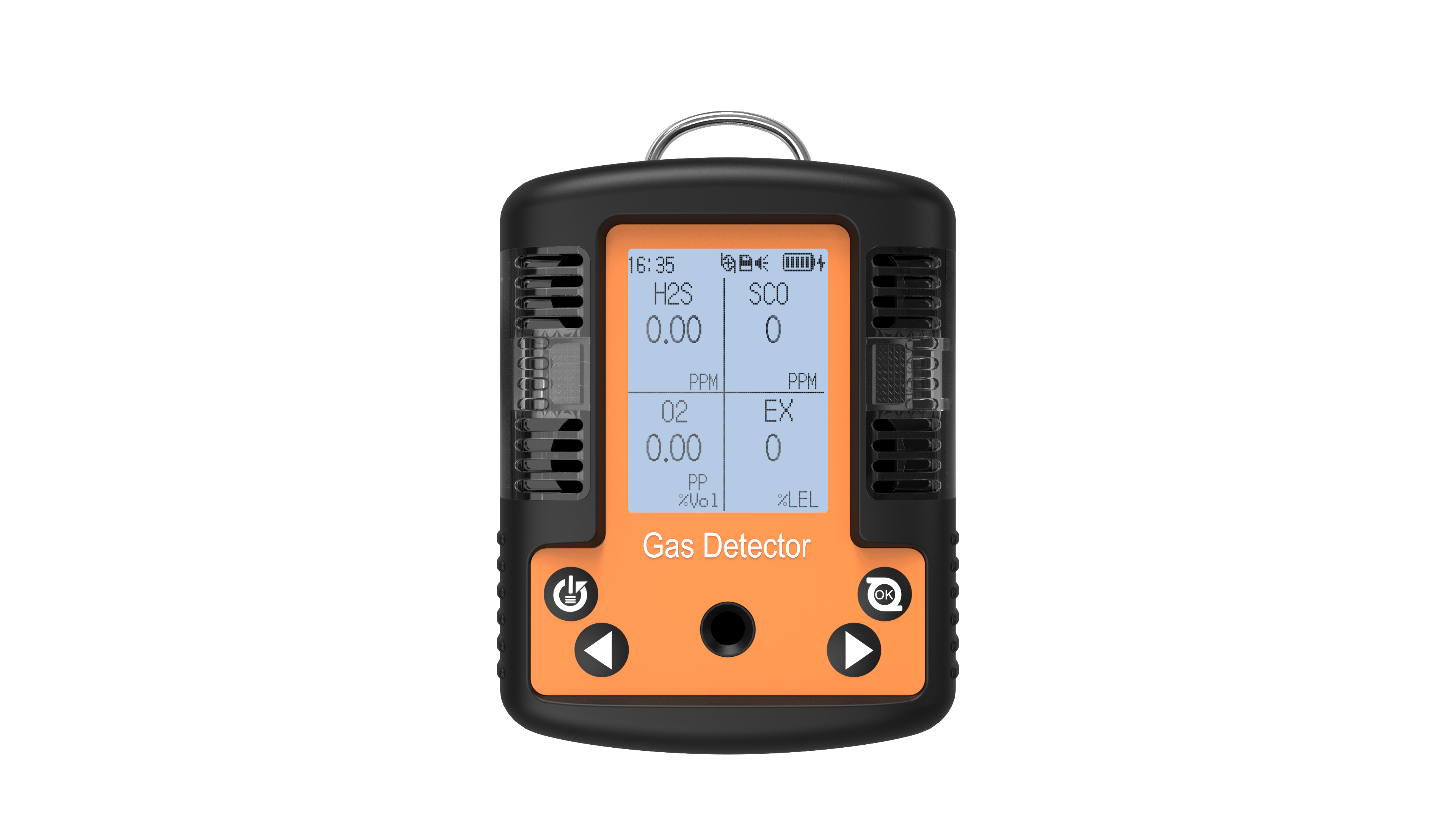
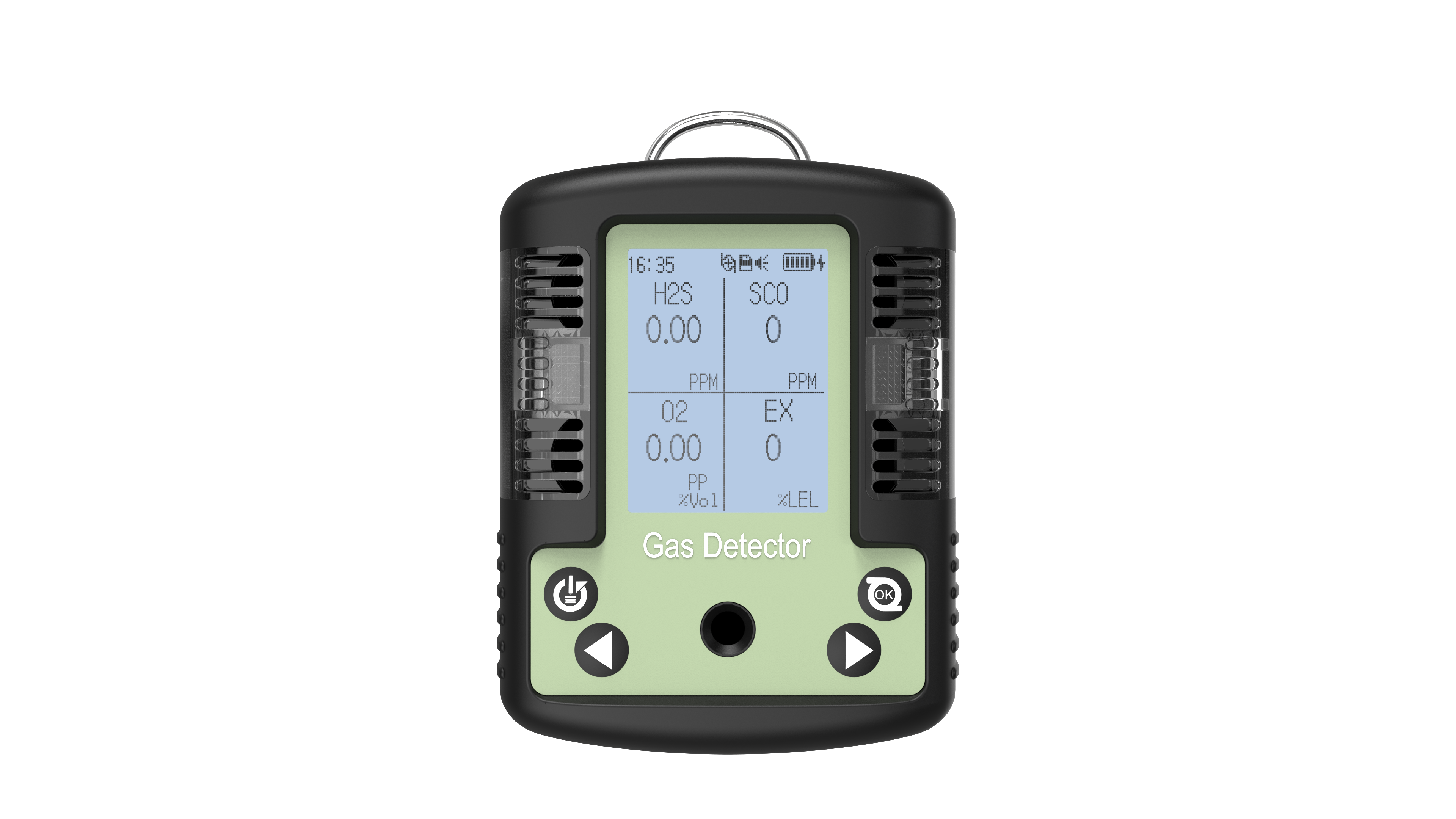
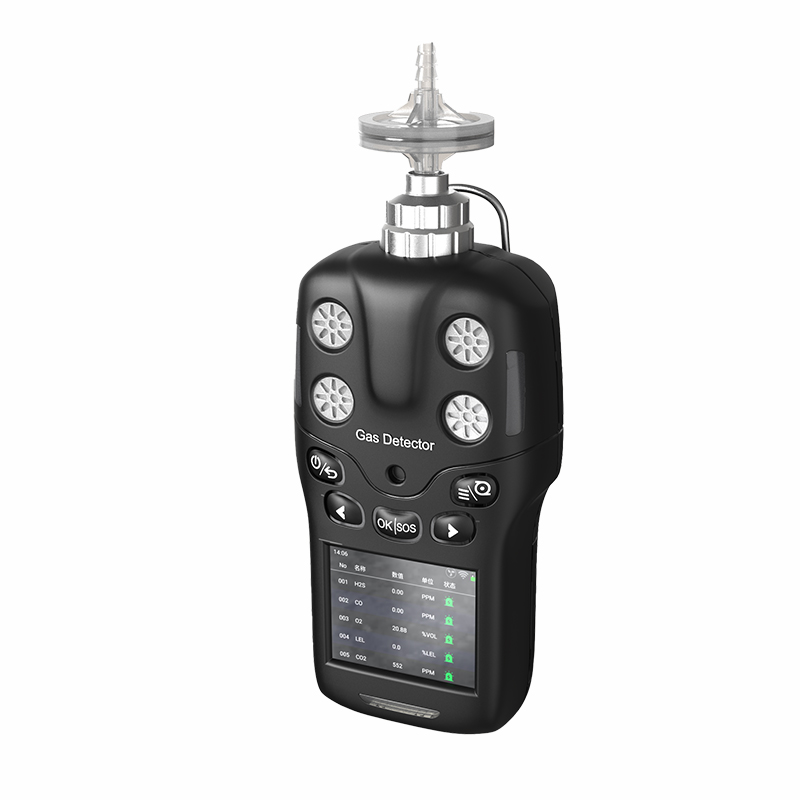
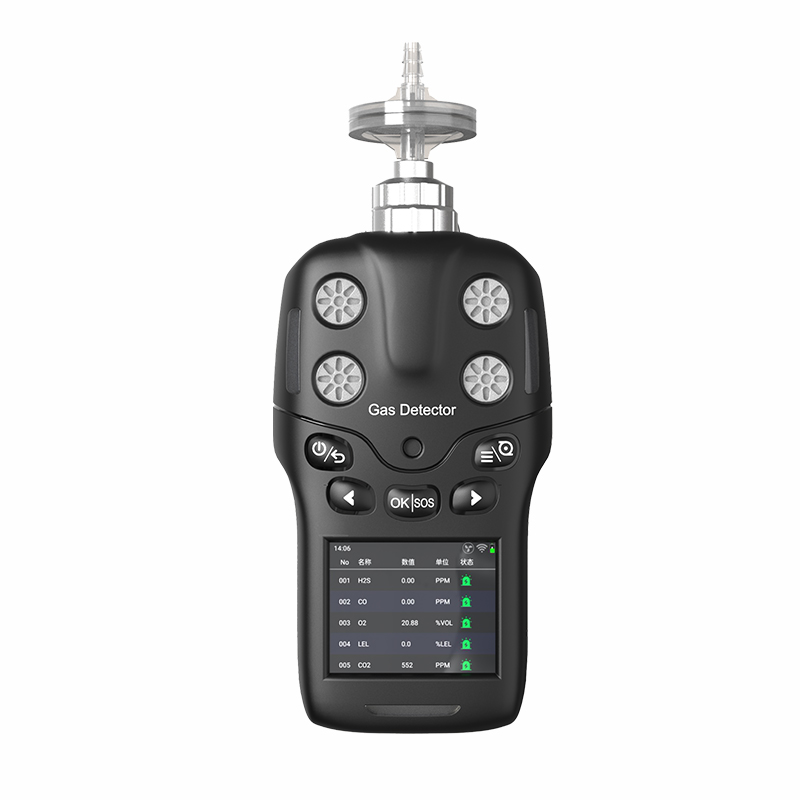
The four-in-one detectors is a portable safety device widely employed across petrochemical, mining, confined space operations, and fire emergency sectors. It simultaneously monitors concentrations of four critical gases—oxygen (O₂), combustible gases (LEL), carbon monoxide (CO), and hydrogen sulphide (H₂S)—providing personnel with real-time environmental safety assessments. For users, understanding the basic functions, application scenarios, key purchasing considerations, and maintenance knowledge of four-in-one detectors not only enhances operational safety but also ensures efficient device performance. The following content provides a systematic introduction to key knowledge regarding four-in-one detectors.
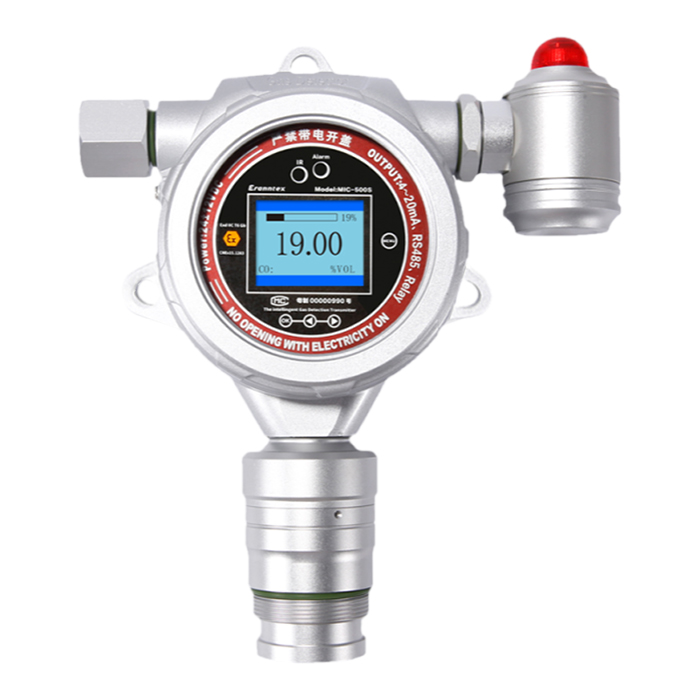

I. Fundamental Functions and Operating Principles of the Quadruple Detector
The quadruple detector is a multi-gas monitoring device whose core function is the real-time surveillance of four critical gases in the air. Oxygen (O₂) monitoring ensures environmental oxygen levels remain within safe parameters (typically 19.5%–23.5%), as concentrations below or above this range pose health hazards to humans; Flammable gas (LEL) monitoring detects potential leaks to prevent explosions or fires; carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrogen sulphide (H₂S) are toxic gases that pose lethal threats even at low concentrations.
These detectors typically employ electrochemical sensors or catalytic combustion sensors, detecting gas concentrations through chemical reactions or resistance changes, then converting the data into digital signals displayed on a screen. When gas concentrations exceed preset alarm thresholds, the device alerts users via audible and visual alarms, vibration, or other means to evacuate immediately or implement emergency measures. Thus, the four-in-one detector serves as an indispensable ‘life-saving instrument’ in industrial safety.
II. Typical Application Scenarios for Four-in-One Detectors
Four-in-one detectors are suitable for diverse high-risk operational environments. Within the petrochemical industry, they are frequently deployed in refineries, chemical plants, storage tank areas, and other flammable and explosive locations. In mining operations, they are deployed in confined spaces like mines and tunnels to prevent oxygen depletion or hazardous gas accumulation; during firefighting and emergency rescue, personnel carry these detectors into fire scenes or accident zones to assess environmental safety in real time; additionally, they monitor potentially toxic gases in sectors such as wastewater treatment, papermaking, and food processing.
For overseas users, operational environments may vary across different countries and regions, making it particularly crucial to select detectors suited to local conditions. For instance, in cold climates, equipment with low-temperature compensation is required; in high-humidity environments, attention must be paid to the detector's waterproof and dustproof rating (e.g., IP67).
III. How to Select the Appropriate Four-in-One Detector?
Selecting a suitable four-in-one detector requires comprehensive consideration of the following aspects:
Sensor Type and Accuracy: High-quality sensors should exhibit high sensitivity, rapid response, and long-term stability. Electrochemical sensors are suitable for toxic gas detection, while catalytic combustion sensors are better suited for combustible gas detection.
Protection Rating: Select an appropriate protection rating based on the operational environment. For instance, IP67-rated equipment offers complete dust protection and can withstand brief immersion in water without damage, making it suitable for harsh conditions.
Alarm Methods: Beyond audible and visual alerts, some devices incorporate vibration alarms, beneficial in high-noise environments. Users may select based on operational requirements.
Data Logging and Transmission: Certain high-end detectors support data storage and USB/Bluetooth transmission, facilitating subsequent analysis and compliance management.
Brand and After-Sales Service: Opting for internationally recognised brands (such as RAE Systems, BW Technologies, Dräger, etc.) ensures product quality while providing comprehensive after-sales support, including calibration services and spare parts supply.
IV. Maintenance and Calibration of Four-in-One Detectors
To ensure detectors remain in optimal working condition, regular maintenance and calibration are essential. Key maintenance recommendations include:
Regular Calibration: Sensors degrade over time; calibration every 3–6 months is advised to maintain detection accuracy. Many national and regional regulations require enterprises to retain calibration records.
Functional Testing (Bump Test): Conduct a bump test before each use to confirm the device can trigger alarms correctly. The test gas concentration should be slightly above the alarm threshold.
Sensor Replacement: Electrochemical sensors typically have a lifespan of 1–3 years. Regular inspections and timely replacements are necessary to prevent false negatives due to sensor failure.
Cleaning and Protection: Keep the device clean to prevent dust or moisture ingress that could impair sensor performance. Using protective covers minimises physical damage.
Battery Management: Regularly check battery charge levels to prevent device shutdown due to low power. During prolonged non-use, charge monthly to prolong battery life.
V. Precautions for Using Four-in-One Detectors
When operating four-in-one detectors, users should observe the following:
Avoid Extreme Environments: Although some devices feature waterproof and dustproof capabilities, prolonged exposure to extreme temperatures, highly corrosive gases, or high-pressure conditions should be avoided.
Correct Wear: Position the detector near the breathing zone (e.g., collar, chest area) to ensure it measures gas concentrations in the air actually breathed by personnel.
Prompt Response to Alarms: Upon device activation, immediately evacuate the hazardous area. Only return after confirming environmental safety to investigate the cause.
Training and Operational Standards: Operators must undergo professional training to understand device functions, alarm meanings, and emergency procedures.
Conclusion
The four-in-one gas detector serves as a vital safety safeguard in modern industrial settings, offering powerful functionality and broad applicability. However, its full potential is realised only through correct selection, scientific operation, and regular maintenance. For overseas users, understanding the detector's fundamentals, selecting appropriate equipment tailored to local working conditions, and establishing comprehensive maintenance plans are key to ensuring operational safety. It is hoped this article enhances your comprehension and usage of four-in-one detectors, making safety a steadfast foundation for every task undertaken.
Related information
-

How to Calibrate an Oxygen Detectors to Ensure Accuracy?
In fields such as industrial safety, confined space operations, environmental monitoring, and even medical support, the measuremen...
2026-01-14 -

What is the measurement range of an oxygen detectors?
Oxygen detectors are indispensable equipment in industrial safety, environmental monitoring, and confined space operations. Accura...
2026-01-13 -

What is the normal oxygen concentration for an oxygen detectors?
Oxygen (O₂) is a vital gas for sustaining human life and most combustion processes. However, both excessively high and low oxygen...
2026-01-12 -

How Do Nitrogen Oxide Detectors Work?
Against a backdrop of growing global concern over air quality and emissions compliance, the precise monitoring of nitrogen oxides ...
2026-01-09 -

Operating Instructions for Nitrogen Oxide Detectors
Nitrogen oxides (NOₓ, primarily comprising nitrogen monoxide NO and nitrogen dioxide NO₂) are significant atmospheric pollutants...
2026-01-07











 info@eranntexgas.com
info@eranntexgas.com

 13480931872
13480931872