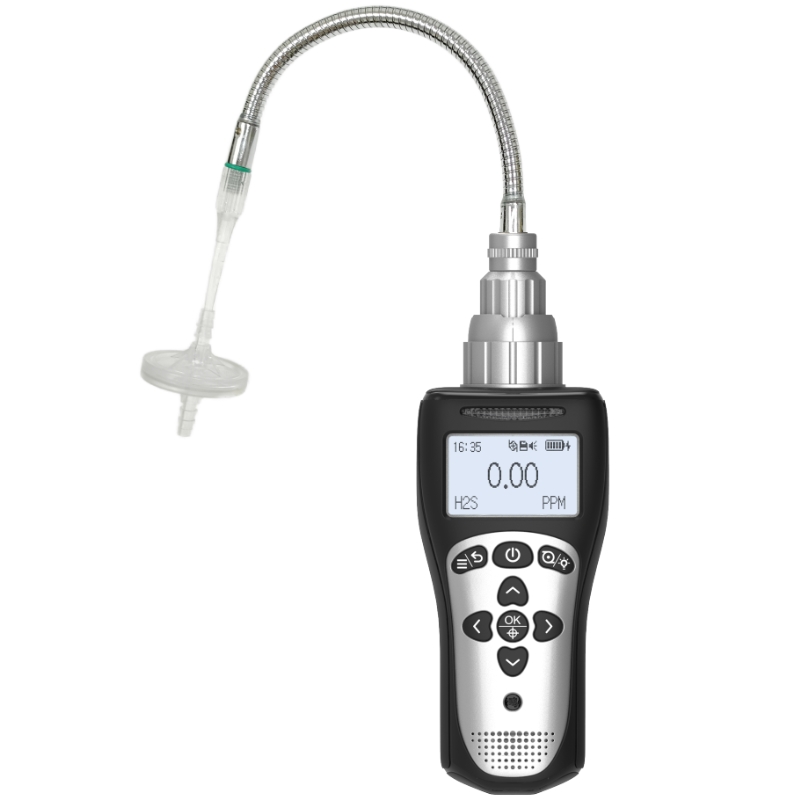
How to Test Your Oxygen Detectors Effectively?
In today's society, where safety and health are paramount, oxygen detectors serve as vital equipment safeguarding us from the dangers of oxygen deficiency or enrichment across diverse environments. Their reliable operation is therefore critical. Regular and effective testing of oxygen detectors ensures precise functioning at crucial moments, providing a vital safety net. Below, Yiyuntian Eranntex details how to effectively test your oxygen detector.

Understanding Testing Intervals and Standards
Testing intervals vary depending on the type and application of the oxygen detector. Generally, detectors used in industrial settings—where operating conditions are complex and harsh—should undergo monthly functional checks and comprehensive calibration every six months. For domestic use, simple tests every three months and annual full calibration are sufficient.
Testing standards primarily adhere to the specifications provided by the equipment manufacturer and relevant local safety regulations. For instance, certain industrial safety standards stipulate that the measurement error of an oxygen detector in normal operating conditions must not exceed ±2%. Understanding these standards provides a clear basis for judgement during testing, ensuring results meet safety requirements.
Visual and Preliminary Inspection
Prior to in-depth testing, conduct a visual inspection of the oxygen detector. Check the housing for damage, cracks, or deformation, as these may compromise the device's seal integrity and affect the normal operation of internal components. Simultaneously, verify that the detector's inlet and outlet ports are unobstructed and free from blockages. If the inlet is clogged with dust or debris, it may impair oxygen sample collection, leading to inaccurate measurements.
Additionally, verify that the display screen and indicator lights function correctly. The screen should clearly show oxygen concentration readings, while indicator lights must illuminate accurately under different statuses (e.g., normal, alarm). Issues such as a blurred display or non-functioning indicator lights may indicate internal circuitry faults requiring further repair.
Functional Testing
Functional testing constitutes the core assessment of an oxygen detector. First, prepare a standard gas sample with a known oxygen concentration, obtainable from professional gas suppliers. Place the detector within the standard gas environment and observe whether the displayed oxygen concentration matches the standard value. If the deviation falls within acceptable limits, the detector's measurement function is operational; excessive deviation necessitates calibration or repair.
Secondly, test the alarm functionality. Most oxygen detectors feature low and high oxygen alarm thresholds. By adjusting the standard gas concentration below the low alarm threshold or above the high alarm threshold, observe whether the detector promptly emits audible and visual alarm signals. The alarm sound should be clear and loud, with distinct flashing lights, ensuring attention is drawn during emergencies.
Battery and Power Supply Inspection
For battery-powered oxygen detectors, battery condition directly impacts operational reliability. Regularly monitor battery charge levels via the device's indicator light or display. Replace batteries promptly when low to prevent critical failure due to depletion.
For detectors powered by an external source, inspect the power cable for integrity, checking for damage or signs of ageing. Simultaneously, ensure the power socket is properly earthed to prevent electrical leakage accidents. Utilise tools such as a multimeter to verify voltage stability and compliance with the device's specified voltage range.
Professional Calibration and Maintenance
Whilst basic checks may be performed independently, regular professional calibration is essential to ensure the accuracy and reliability of oxygen detectors. Specialised calibration technicians possess advanced equipment and extensive experience to conduct comprehensive, precise calibration. This adjusts measurement parameters, restoring the detector to optimal operational condition.
Additionally, routine maintenance is crucial during daily operation. Avoid exposing the detector to corrosive substances, high temperatures, or strong magnetic fields, as these conditions may damage internal components. Regularly clean the detector housing and air intake to maintain hygiene and prevent contamination.
Effective oxygen detector maintenance requires knowledge of specific procedures and strict adherence to testing schedules and standards. Through regular visual inspections, functional tests, battery and power checks, alongside professional calibration and servicing, you can ensure your oxygen detector remains in optimal working order, creating a safe and reliable environment for yourself and those around you.
Related information
-

How to Calibrate an Oxygen Detectors to Ensure Accuracy?
In fields such as industrial safety, confined space operations, environmental monitoring, and even medical support, the measuremen...
2026-01-14 -

What is the measurement range of an oxygen detectors?
Oxygen detectors are indispensable equipment in industrial safety, environmental monitoring, and confined space operations. Accura...
2026-01-13 -

What is the normal oxygen concentration for an oxygen detectors?
Oxygen (O₂) is a vital gas for sustaining human life and most combustion processes. However, both excessively high and low oxygen...
2026-01-12 -

How Do Nitrogen Oxide Detectors Work?
Against a backdrop of growing global concern over air quality and emissions compliance, the precise monitoring of nitrogen oxides ...
2026-01-09 -

Operating Instructions for Nitrogen Oxide Detectors
Nitrogen oxides (NOₓ, primarily comprising nitrogen monoxide NO and nitrogen dioxide NO₂) are significant atmospheric pollutants...
2026-01-07











 info@eranntexgas.com
info@eranntexgas.com

 13480931872
13480931872