Tips for Maintaining Your 4-in-1 Detectors
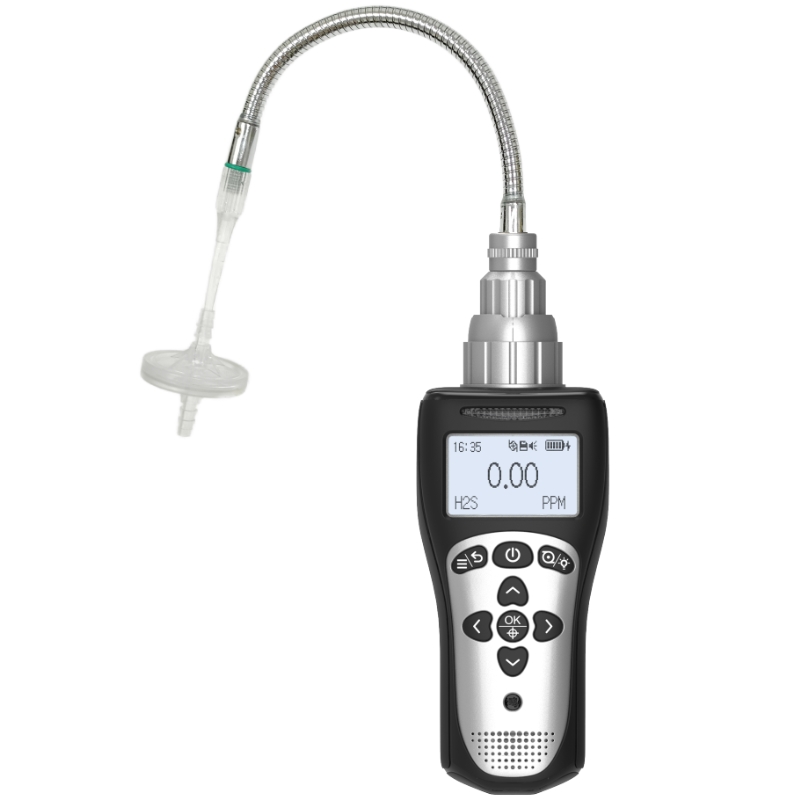
The four-in-one detector (typically capable of simultaneously monitoring oxygen, combustible gases, carbon monoxide, and hydrogen sulphide) is a portable safety device widely employed in industrial safety, petrochemical operations, mining, and confined space work. It provides real-time gas concentration monitoring in hazardous environments, issuing timely warnings of potential risks to safeguard personnel. However, ensuring the detector remains in optimal working condition necessitates regular maintenance and servicing. This article provides a series of practical maintenance tips to assist overseas users in scientifically and efficiently managing their four-in-one gas detectors, ensuring their long-term stable operation.

1. Regular Calibration Testing
Undergo professional calibration at intervals recommended by the manufacturer (typically every 6-12 months) to verify sensor accuracy for detecting combustible gases, oxygen, carbon monoxide, and hydrogen sulphide. Cross-verify using standard gases to prevent false alarms or missed detections caused by sensor drift.
2. Clean Sensors and Air Inlets
Weekly clean the detector casing and air inlets with a soft-bristled brush or compressed air to remove dust and grease, preventing particulate blockages. Avoid solvents or corrosive cleaners to prevent damage to sensitive components.
3. Check Battery Status
Confirm sufficient battery charge before each use (recommended to maintain above 50%). For long-term storage, recharge every three months to prevent battery degradation. Where replaceable batteries are supported, prioritise original manufacturer batteries or certified alternatives.
4. Avoid Extreme Environments
Prevent exposure to high temperatures (>50°C), low temperatures (<-20°C), high humidity (>95% RH), or corrosive gases, as these conditions may accelerate sensor degradation. For harsh environments, select models with an IP67 or higher protection rating.
5. Maintain a maintenance log
Establish a device maintenance record, documenting calibration dates, fault codes, replaced components, and other relevant information. Analyse data to predict sensor lifespan proactively. For instance, electrochemical sensors typically last 2-3 years, while catalytic combustion sensors last 3-5 years.
6. Impact and Drop Protection
Fit detectors with protective casings to prevent internal component loosening from falls. Use dedicated transport cases with sensor position securing to minimise vibration impact.
7. Software Updates and Firmware Upgrades
Periodically connect to the manufacturer's software platform (e.g., via USB or Bluetooth) to download the latest firmware for optimised algorithm performance. Certain models support automatic alarm threshold adjustment; ensure software version compatibility.
8. Pre-storage Preparation
Prior to extended storage, operate the detector in a clean, dry environment (temperature 20-25°C, humidity 40-60%) for 24 hours to expel internal moisture. Remove batteries and store separately to prevent leakage from corroding circuitry.
9. Professional Maintenance and Component Replacement
Upon encountering error codes such as E1 (sensor failure) or E2 (circuit anomaly), cease operation immediately and contact an authorised service centre. Never disassemble the device yourself, particularly components involving explosion-proof structures.
10. User Training and Operational Protocols
Conduct regular operator training emphasising the standard procedure: ‘Power-on self-test → Wear check → Area detection → Power-off cleaning’. Avoid obstructing air inlets or concealing alarm lights/sirens during testing.
The four-in-one gas detector is a vital tool for industrial safety, yet its effectiveness relies on scientific maintenance and upkeep. Through regular calibration, sensor checks, protective cleaning, battery management, and functional testing, overseas users can ensure detectors remain in optimal working condition, providing reliable safety assurance for personnel. Safety is no trivial matter. Establishing a comprehensive maintenance plan is not only a responsibility towards life but also safeguards corporate compliance and operational efficiency. We hope these tips assist you in better managing your four-in-one gas detectors, ensuring safety accompanies every task you undertake.
Related information
-

How to Calibrate an Oxygen Detectors to Ensure Accuracy?
In fields such as industrial safety, confined space operations, environmental monitoring, and even medical support, the measuremen...
2026-01-14 -

What is the measurement range of an oxygen detectors?
Oxygen detectors are indispensable equipment in industrial safety, environmental monitoring, and confined space operations. Accura...
2026-01-13 -

What is the normal oxygen concentration for an oxygen detectors?
Oxygen (O₂) is a vital gas for sustaining human life and most combustion processes. However, both excessively high and low oxygen...
2026-01-12 -

How Do Nitrogen Oxide Detectors Work?
Against a backdrop of growing global concern over air quality and emissions compliance, the precise monitoring of nitrogen oxides ...
2026-01-09 -

Operating Instructions for Nitrogen Oxide Detectors
Nitrogen oxides (NOₓ, primarily comprising nitrogen monoxide NO and nitrogen dioxide NO₂) are significant atmospheric pollutants...
2026-01-07











 info@eranntexgas.com
info@eranntexgas.com

 13480931872
13480931872