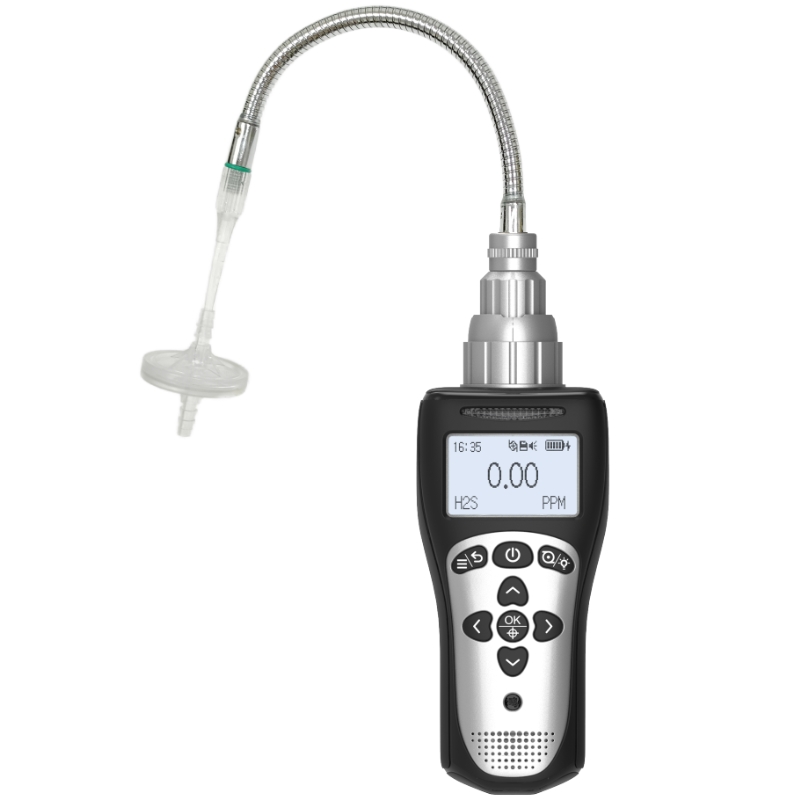
How to use a Combustible Gas Detectors?
In Western countries, Combustible gas detectors serve as vital safety equipment across households, industrial sites, and commercial premises. Proper utilisation ensures timely alerts during gas leaks, preventing severe incidents such as fires and explosions. Below, Yiyuntian Eranntex provides a detailed guide on operating combustible gas detectors.
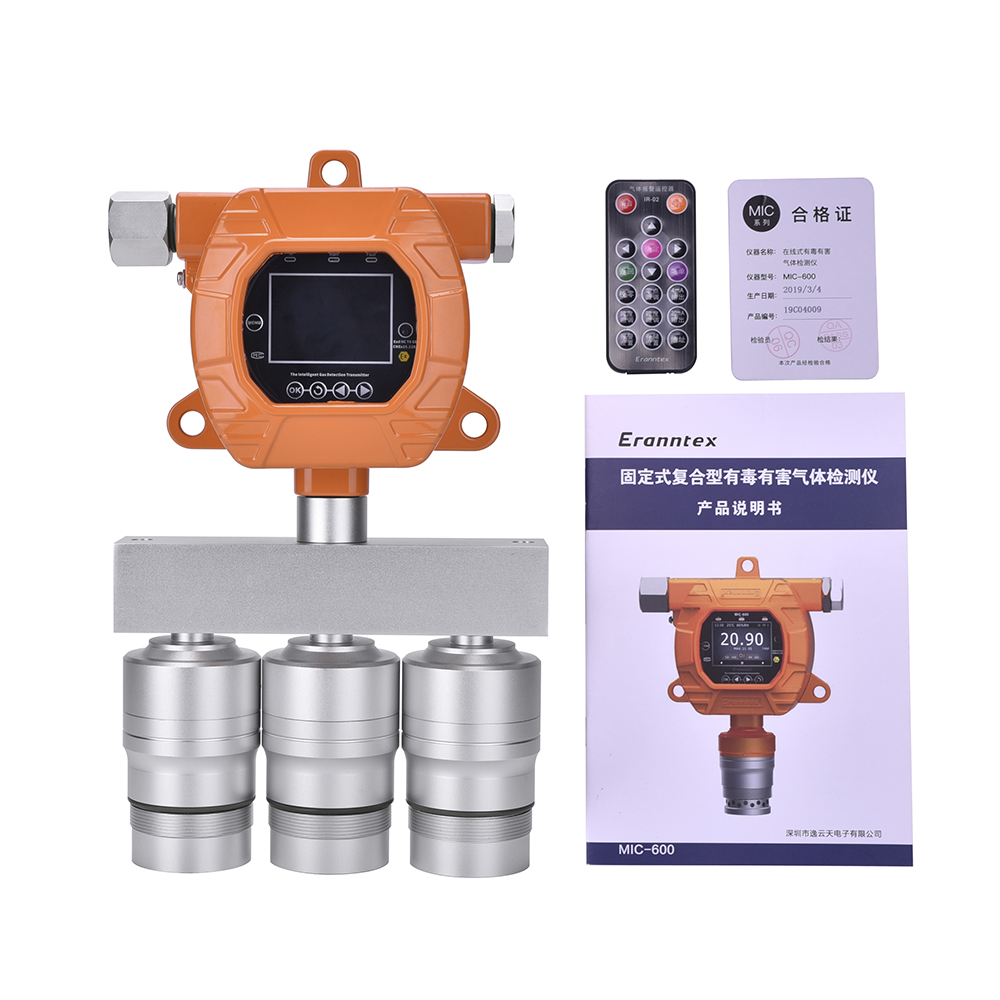

I. Preparations Before Installation
1. Understanding Applicable Scenarios and Gas Types
Different models of combustible gas detectors are designed to detect specific gases. For instance, some are tailored for natural gas (primarily methane), while others are more sensitive to liquefied petroleum gas (LPG, mainly propane and butane). Before purchasing, clearly identify the gas type requiring detection and select the corresponding product. Simultaneously, consider the usage environment. Different settings—such as domestic kitchens, industrial workshops, or underground car parks—impose varying demands on detector performance and installation locations.
2. Inspect Equipment Integrity
Upon receiving the detector, meticulously examine the packaging for integrity. Check the detector's exterior for damage or scratches and verify that all accessories are present. Typically, detectors come equipped with a manual, mounting bracket, screws, and other components. Should any damage or missing components be discovered, promptly contact the supplier for replacement.
3. Read the instruction manual
This is a crucial step. Different brands and models of combustible gas detectors may vary in operating procedures, function settings, and alarm threshold adjustments. Carefully review the manual to understand the detector's fundamental parameters, operating principles, operational steps, and precautions, laying the groundwork for correct usage.
II. Installation Process
1. Selecting an Appropriate Installation Location
Domestic Settings: For detecting natural gas, install the detector in the kitchen near gas pipelines and appliances, approximately 30 centimetres below the ceiling. As natural gas is lighter than air, it disperses upwards. For detecting liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), which is heavier than air, install the detector approximately 30 centimetres above the floor near potential leakage points, such as near gas cylinders.
Industrial Settings:
Detection points should be determined based on production processes and potential gas leakage locations. Typically, detectors are installed at gas pipeline connections, near valves, and at equipment exhaust points. Ventilation conditions must also be considered; avoid installation in poorly ventilated corners to prevent compromised detection performance.
2. Securing the Detector
Secure the detector to the selected location using mounting brackets and screws. Ensure a firm installation to prevent swaying or detachment during operation. Pay attention to the detector's orientation during installation; the correct direction is typically indicated in the manual. Installing according to specifications ensures proper sensor function.
3. Connecting the Power Supply (for mains-powered detectors)
Some detectors operate on batteries, while others require mains connection. For mains-powered units, connect the wiring correctly according to the manual, ensuring secure connections and adequate insulation. After connection, verify the power indicator illuminates to confirm the detector is energised.
III. Operation and Calibration
1. Power-up and Self-Test
Upon connecting to mains power or inserting batteries, the detector will automatically power on and perform a self-test. During this process, the indicator light will flash and a brief alarm may sound – both are normal phenomena. After the self-test completes, the detector enters normal operational mode, with the indicator light remaining steadily illuminated or flashing according to the preset pattern.
2. Setting Alarm Thresholds (For Select Adjustable Models)
Some advanced combustible gas detectors permit users to configure alarm thresholds according to operational requirements. Access the configuration mode via the detector's buttons or remote control, following the manual's instructions, to adjust the alarm threshold. After configuration, conduct a test to verify the alarm function operates correctly.
3. Periodic Testing
To ensure the detector remains in optimal working condition, conduct regular testing. Use specialised test gas or perform simulated tests following the methods outlined in the manual. Position the test gas near the detector's sensor and observe whether the alarm activates within the specified timeframe. Should the test fail, promptly contact a qualified technician for repair or replacement.
IV. Routine Maintenance
1. Cleaning the Detector
Regularly wipe the detector housing with a clean, soft cloth to remove dust and grime. Avoid using chemical cleaners or organic solvents, as these may damage the housing or sensor.
2. Replace Batteries (if battery-powered)
Replace batteries periodically as specified in the manual to ensure sufficient power for normal operation. When replacing batteries, pay attention to the correct polarity orientation to prevent incorrect installation.
3. Periodic Calibration
It is generally recommended to calibrate the detector annually to ensure detection accuracy. Calibration requires specialised equipment and technical personnel; contact the manufacturer or an authorised service centre for this procedure.
Proper use and routine maintenance of combustible gas detectors are essential for maximising their safety benefits. We urge everyone to take this responsibility seriously, safeguarding both personal and public life and property.
Related information
-

How to Calibrate an Oxygen Detectors to Ensure Accuracy?
In fields such as industrial safety, confined space operations, environmental monitoring, and even medical support, the measuremen...
2026-01-14 -

What is the measurement range of an oxygen detectors?
Oxygen detectors are indispensable equipment in industrial safety, environmental monitoring, and confined space operations. Accura...
2026-01-13 -

What is the normal oxygen concentration for an oxygen detectors?
Oxygen (O₂) is a vital gas for sustaining human life and most combustion processes. However, both excessively high and low oxygen...
2026-01-12 -

How Do Nitrogen Oxide Detectors Work?
Against a backdrop of growing global concern over air quality and emissions compliance, the precise monitoring of nitrogen oxides ...
2026-01-09 -

Operating Instructions for Nitrogen Oxide Detectors
Nitrogen oxides (NOₓ, primarily comprising nitrogen monoxide NO and nitrogen dioxide NO₂) are significant atmospheric pollutants...
2026-01-07











 info@eranntexgas.com
info@eranntexgas.com

 13480931872
13480931872