How long does a carbon monoxide detectors last?
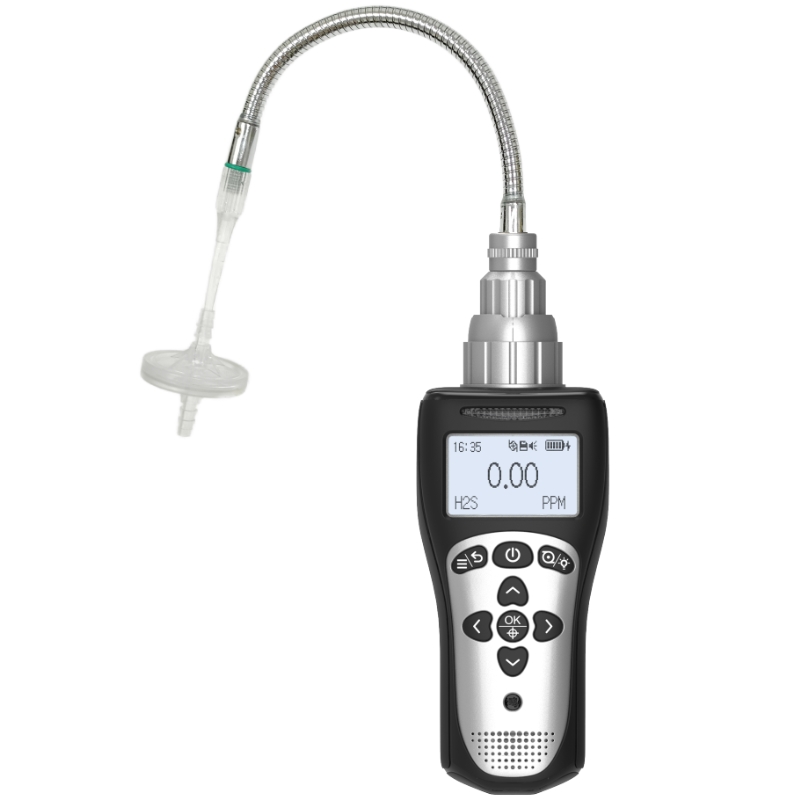
In industrial safety, carbon monoxide (CO) detectors serve as core equipment for preventing acute poisoning incidents. According to the International Labour Organization (ILO), over 1,200 fatalities occur annually worldwide due to CO leaks in industrial settings. Companies equipped with reliable detection systems can reduce accident rates by 76%. Below, Yiyuntian Eranntex's editor systematically analyzes the lifespan management of industrial-grade carbon monoxide detectors from three dimensions: sensor technology, industrial environmental impacts, and maintenance strategies.

I. Sensor Technology Determines Fundamental Lifecycle
Industrial-grade detectors primarily employ two technical approaches: electrochemical sensors and infrared sensors. Their differing lifespans stem from distinct operating principles. Electrochemical sensors generate electrical signals through redox reactions between CO molecules and electrolytes, typically lasting 2-5 years. However, actual performance is significantly impacted by prolonged exposure to high concentrations in industrial settings.
Infrared sensors leverage CO molecules' specific absorption of 4.66-micrometer infrared light, achieving precise detection via dual-beam differential measurement. These sensors generally last at least 5 years and offer superior resistance to cross-interference. Tests by Germany's TÜV industrial laboratory show that in mixed gases containing 200ppm methane and 500ppm carbon dioxide, infrared sensors exhibit only one-fifth the zero-point drift of electrochemical sensors. This makes them the preferred solution for heavy industries such as petrochemicals and metallurgy.
New solid-state sensor technologies are breaking traditional lifespan constraints. Honeywell's metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) sensors detect CO molecules by measuring conductivity changes caused by adsorption, achieving an 8-year lifespan at 300°C operating temperatures.
II. Mechanisms Accelerating Equipment Aging in Industrial Environments
Complex industrial environments pose multiple challenges to sensor longevity. In paper mills and food processing plants where humidity consistently exceeds 80%, the evaporation rate of electrochemical sensor electrolytes accelerates, causing sensitivity degradation to occur 1-2 years earlier.
Dust contamination is a common issue in metallurgical and mining industries. Research by the U.S. National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) indicates that metal particles smaller than 5 microns embed into sensor surfaces, prolonging response times by 40%. Chilean copper mines employ a three-stage filtration system: an outer pre-filter captures large particles, an intermediate electrostatic layer adsorbs PM2.5, and an inner HEPA filter achieves 99.97% particle interception. This enables equipment to maintain a 3-year effective lifespan even in environments with dust concentrations reaching 100mg/m³.
III. Industrial-Grade Maintenance Strategies and Lifecycle Management
Regular calibration is essential for maintaining detection accuracy. British Standards Institution (BSI) industrial safety regulations mandate functional testing with standard gases every three months for detectors in high-risk areas, while equipment in critical process stages requires monthly calibration. MSA's S4000CH detector, customized for refineries, incorporates an automatic calibration module. It adjusts zero points and ranges via wireless connection to calibration stations, reducing annual maintenance costs by 45%.
Sensor replacement timing requires data-driven monitoring. Industrial detectors developed by Germany's Draeger feature self-diagnostic systems that trigger dual alerts—audible/visual alarms and 4-20mA signal—when sensor sensitivity drops to 80% of initial value.
IV. Global Industrial Market Selection Guide
For the EU market, select equipment compliant with EN 60079-29-1:2016. This standard mandates sensors pass -30°C low-temperature and 70°C high-temperature tests, plus 90 days of continuous operation without failure in 95% humidity environments. In North America, verify UL 2075 certification, which requires devices to feature self-diagnostics, terminal voltage monitoring, and electromagnetic interference (EMI) resistance.
When selecting equipment, match the protection rating to process characteristics. Chemical facilities should use explosion-proof equipment with IP66 protection, while metallurgical industries require sensor modules resistant to high temperatures (≥120°C). For continuous monitoring needs, consider devices with data logging capabilities.
Technologically, laser-based spectral sensors are increasingly dominating the high-end industrial market. Utilizing Tunable Diode Laser Absorption Spectroscopy (TDLAS), these devices achieve ppb-level detection accuracy with lifespans exceeding 10 years.
The lifespan management of industrial-grade carbon monoxide detectors fundamentally involves achieving a dynamic equilibrium between technical reliability, environmental adaptability, and economic viability. Through scientific selection, standardized maintenance, and forward-looking technological upgrades, enterprises can not only establish a dependable safety defense but also maximize the full lifecycle value of their detection systems. As the International Industrial Safety Association (IISA) cautions: “In industry, a detector's lifespan is measured not in years, but in the continuity of safety it ensures.”
Related information
-

How to Calibrate an Oxygen Detectors to Ensure Accuracy?
In fields such as industrial safety, confined space operations, environmental monitoring, and even medical support, the measuremen...
2026-01-14 -

What is the measurement range of an oxygen detectors?
Oxygen detectors are indispensable equipment in industrial safety, environmental monitoring, and confined space operations. Accura...
2026-01-13 -

What is the normal oxygen concentration for an oxygen detectors?
Oxygen (O₂) is a vital gas for sustaining human life and most combustion processes. However, both excessively high and low oxygen...
2026-01-12 -

How Do Nitrogen Oxide Detectors Work?
Against a backdrop of growing global concern over air quality and emissions compliance, the precise monitoring of nitrogen oxides ...
2026-01-09 -

Operating Instructions for Nitrogen Oxide Detectors
Nitrogen oxides (NOₓ, primarily comprising nitrogen monoxide NO and nitrogen dioxide NO₂) are significant atmospheric pollutants...
2026-01-07










 info@eranntexgas.com
info@eranntexgas.com

 13480931872
13480931872