Can a carbon dioxide detectors detect other gases?
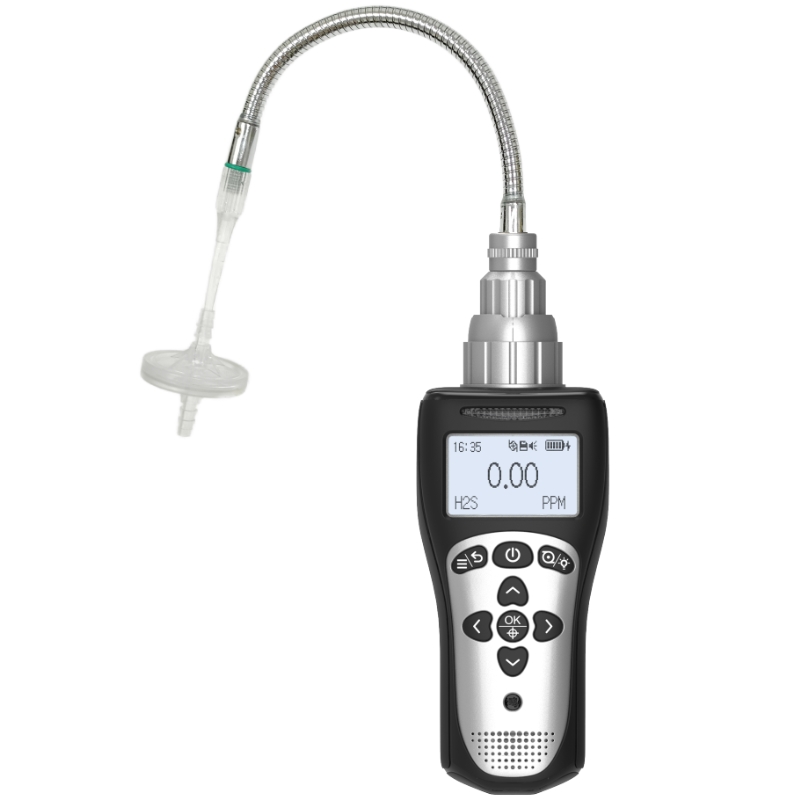
In the field of industrial operations, ensuring a safe and well-monitored working environment is crucial. Among the various tools and equipment used for this purpose, carbon dioxide detectors have become a key component. For those deeply involved in the industrial sector, a fundamental question often arises: can a carbon dioxide detector really detect gases? Below, Yiyuntian Eranntex will provide a detailed explanation.

The Core Function of a Carbon Dioxide Detector
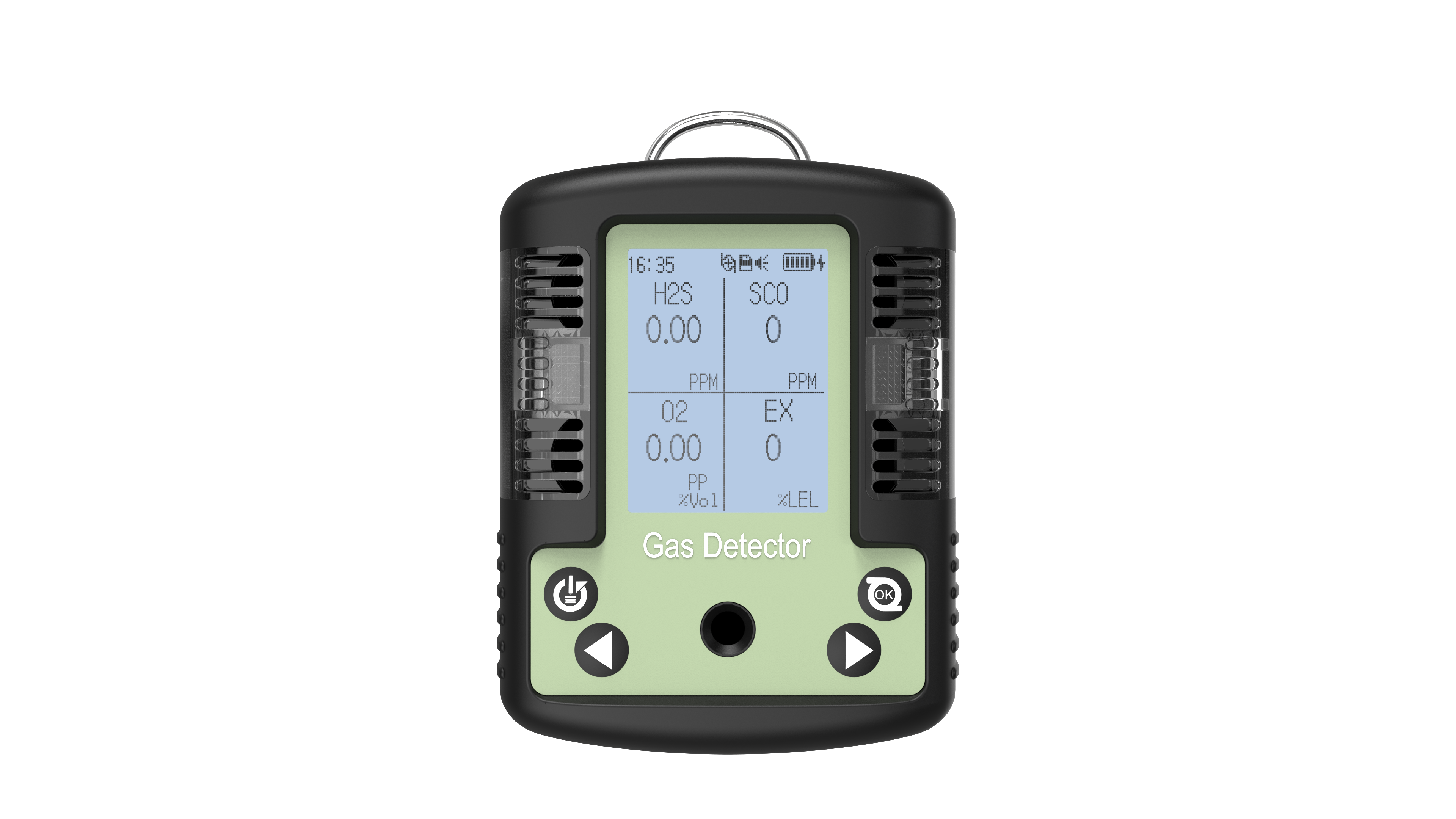
Essentially, a carbon dioxide detector is specifically designed to detect a particular gas—carbon dioxide (CO₂). In industrial environments, the sources of carbon dioxide are diverse. For example, in breweries and wineries, microorganisms break down sugars during fermentation, releasing carbon dioxide as a byproduct. In some chemical manufacturing plants, chemical reactions can also release large amounts of carbon dioxide. If the concentration of carbon dioxide in the air exceeds safe levels, it poses a serious threat to the health and safety of workers. High concentrations of carbon dioxide can cause dizziness, shortness of breath, and in extreme cases, even suffocation. Therefore, the primary and direct function of a carbon dioxide detector is to accurately measure the concentration of carbon dioxide gas in the air of industrial environments.
Detection Principles Enable Accurate Detection
The ability of a carbon dioxide detector to detect gases is due to its advanced detection principles. One common type is based on infrared (IR) sensors. Carbon dioxide molecules have a unique characteristic: they absorb infrared light at specific wavelengths. When infrared light shines on an air sample containing carbon dioxide, the amount of light absorbed is proportional to the concentration of carbon dioxide in the air. The detector measures the intensity of the transmitted light and uses this information to calculate the concentration of carbon dioxide. This principle allows the detector to perform highly accurate and reliable detection of carbon dioxide gas, even in complex industrial environments where other gases are present.
Another type is based on electrochemical sensors. In an electrochemical carbon dioxide sensor, carbon dioxide gas reacts chemically with the electrolyte inside the sensor. This reaction produces an electric current, and the magnitude of the current is related to the concentration of carbon dioxide. By measuring the electrical signal, the detector can determine the amount of carbon dioxide in the air. These advanced detection principles ensure that carbon dioxide detectors can effectively differentiate between carbon dioxide and other gases, providing accurate readings.
Practical Applications in Industrial Environments
In real-world industrial settings, the ability of carbon dioxide detectors to detect gases has been repeatedly verified. In underground mining operations, where ventilation is crucial, carbon dioxide detectors are installed in various locations to continuously monitor carbon dioxide concentrations. If the concentration begins to rise, it may indicate a problem with the ventilation system or the presence of a fire or other source of carbon dioxide. This early warning allows miners to take immediate action, such as evacuating the area or adjusting the ventilation system, to prevent potential disasters.
In large warehouses and cold storage facilities, carbon dioxide detectors are used to monitor air quality. In these environments, forklifts and other equipment may use propane or other fuels, which produce carbon dioxide when burned. Additionally, stored agricultural products release carbon dioxide through respiration. By detecting the gas, the detectors help maintain a safe working environment for employees and ensure the quality of stored goods.
In some chemical production plants, different chemical reactions may produce carbon dioxide as a product or byproduct. Carbon dioxide detectors can monitor the concentration of carbon dioxide during the reaction process in real time, helping operators adjust reaction conditions promptly to ensure the safety and stability of the production process. If the carbon dioxide concentration rises abnormally, it may indicate a runaway reaction or other safety hazards, allowing operators to quickly take measures to prevent accidents.
In summary, carbon dioxide detectors do indeed possess the ability to detect gases, particularly carbon dioxide. Their carefully designed detection principles and proven track record in industrial applications make them an indispensable tool for ensuring safety and quality in the industrial sector.
Related information
-

How to Calibrate an Oxygen Detectors to Ensure Accuracy?
In fields such as industrial safety, confined space operations, environmental monitoring, and even medical support, the measuremen...
2026-01-14 -

What is the measurement range of an oxygen detectors?
Oxygen detectors are indispensable equipment in industrial safety, environmental monitoring, and confined space operations. Accura...
2026-01-13 -

What is the normal oxygen concentration for an oxygen detectors?
Oxygen (O₂) is a vital gas for sustaining human life and most combustion processes. However, both excessively high and low oxygen...
2026-01-12 -

How Do Nitrogen Oxide Detectors Work?
Against a backdrop of growing global concern over air quality and emissions compliance, the precise monitoring of nitrogen oxides ...
2026-01-09 -

Operating Instructions for Nitrogen Oxide Detectors
Nitrogen oxides (NOₓ, primarily comprising nitrogen monoxide NO and nitrogen dioxide NO₂) are significant atmospheric pollutants...
2026-01-07











 info@eranntexgas.com
info@eranntexgas.com

 13480931872
13480931872