Do carbon dioxide detectors expire?
Amidst the global industrial boom and increasingly stringent workplace safety and environmental quality controls, carbon dioxide detectors have become essential equipment across numerous industrial sectors for ensuring production safety and maintaining environmental stability. For practitioners and enterprises abroad who prioritise industrial production standards and personnel safety, a common and critical question arises: Do carbon dioxide detectors expire? Below, Yiyuntian Eranntex provides an explanation.

Hardware Composition and Potential Degradation
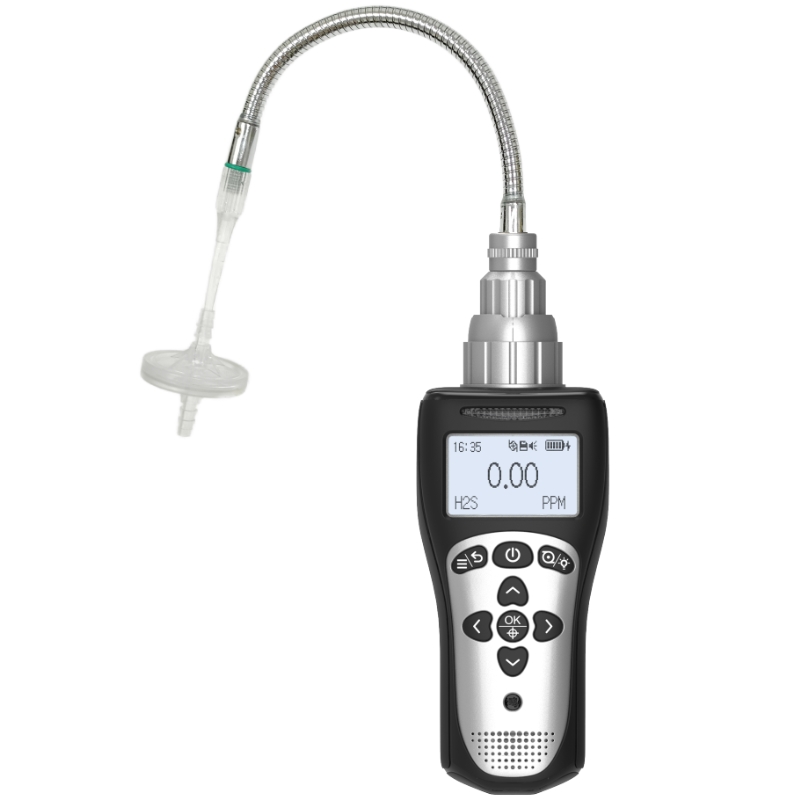
Carbon dioxide detectors typically comprise sensors, circuit boards, display screens, and casings. The sensor, as the core component, bears the responsibility of detecting atmospheric carbon dioxide concentrations and converting them into electrical signals. In industrial settings, common sensors include electrochemical and infrared variants.
Electrochemical sensors contain specific chemical compounds that gradually degrade and deteriorate over time and with usage. In industrial settings, where CO₂ levels may fluctuate frequently, sensors must continuously monitor and respond, accelerating the depletion of these internal chemicals. Much like a machine operating under heavy loads experiences accelerated component wear, electrochemical sensors exhibit a noticeable decline in detection accuracy and response speed after prolonged use, failing to accurately reflect ambient CO₂ concentrations.
Infrared sensors, while relatively more stable, face challenges in complex industrial settings. Contaminants such as dust and oil residues readily adhere to sensor surfaces, impairing infrared absorption and reflection, thereby introducing measurement inaccuracies. Furthermore, mechanical stresses like vibration and impact present in industrial environments may damage the internal structure of infrared sensors, adversely affecting their performance.
The circuit board, serving as the detector's “brain”, processes signals from sensors and displays results. Within industrial settings, circuit boards face multiple challenges. High temperatures accelerate component ageing, altering parameter values and causing circuit instability; humid air may cause moisture ingress, leading to short circuits; furthermore, electromagnetic interference present in industrial environments can disrupt normal circuit board operation, compromising the detector's accuracy and reliability.
The display screen provides a visual representation of carbon dioxide concentration levels. Prolonged use may result in blurred visuals, flickering, or even complete blackouts. Within industrial settings, the screen may also sustain physical damage from impacts or scratches, further compromising functionality. While seemingly straightforward, the housing plays a vital role in safeguarding internal components. Corrosive gases and chemicals present in industrial environments may corrode the casing, compromising its protective function. This exposes internal components to harsh conditions, accelerating their deterioration.
Impact of Operating Environment on Detector Lifespan
Industrial environments are complex and varied, with different industrial settings exerting distinct influences on the lifespan of carbon dioxide detectors. In chemical plants, air may contain high concentrations of corrosive gases such as chlorine or hydrogen sulphide. These gases not only directly corrode the detector's sensors and circuit boards but also react with internal chemical compounds, causing sensor failure. For instance, chlorine reacts chemically with certain components in electrochemical sensors, damaging their structure and impairing their ability to accurately measure CO₂ concentrations.
In underground workplaces such as mines and tunnels, air humidity is typically high and dust levels may be substantial. High humidity environments readily cause internal components to become damp, triggering issues like short circuits; dust, meanwhile, adheres to sensor surfaces, compromising detection accuracy. Furthermore, poor ventilation in subterranean settings facilitates carbon dioxide accumulation, necessitating prolonged continuous operation of the detector. This undoubtedly increases operational strain and accelerates component ageing.
In high-temperature smelting industries, such as steelworks and non-ferrous metal smelters, operating environments feature elevated temperatures. Heat degrades the performance of electronic components, softens and deforms plastic casings, and may even render detectors inoperable. Moreover, high temperatures accelerate the volatilisation and degradation of internal chemical compounds within sensors, shortening their service life.
The Importance of Regular Calibration and Maintenance
Even if a carbon dioxide detector has not reached its strict ‘expiry’ date, regular calibration and maintenance remain essential. In industrial production, accurate CO₂ concentration detection is paramount. Should the detector's readings deviate, personnel may misjudge environmental conditions, potentially triggering safety incidents. For instance, during confined space operations, if elevated CO₂ levels go undetected, workers could suffer asphyxiation due to oxygen deprivation.
Regular calibration adjusts the detector's parameters to restore accurate measurement capability. Generally, industrial CO₂ detectors should be calibrated every six months to one year, with the specific interval adjusted according to usage environment and frequency. Calibration must be performed by professional metrology institutions or the equipment manufacturer to ensure accuracy and reliability.
Routine maintenance is equally vital. Regularly clean the detector's casing and sensor surface to prevent dust and grime accumulation; check battery levels and replace batteries promptly to ensure normal operation; inspect connection cables for looseness or damage, repairing or replacing them immediately if issues arise.
While carbon dioxide detectors do not have a strict ‘expiry date’ in the traditional sense, their performance gradually deteriorates due to hardware ageing, environmental influences, and lack of regular calibration and maintenance. To ensure accurate and reliable operation, safeguarding industrial production safety and stability, it is advisable to calibrate and maintain the detector regularly according to its manual and operating environment. Replace the detector promptly when significant performance degradation is observed. This approach enables carbon dioxide detectors to continue fulfilling their vital role in industrial settings, providing essential protection for manufacturing processes.
Related information
-

How to Calibrate an Oxygen Detectors to Ensure Accuracy?
In fields such as industrial safety, confined space operations, environmental monitoring, and even medical support, the measuremen...
2026-01-14 -

What is the measurement range of an oxygen detectors?
Oxygen detectors are indispensable equipment in industrial safety, environmental monitoring, and confined space operations. Accura...
2026-01-13 -

What is the normal oxygen concentration for an oxygen detectors?
Oxygen (O₂) is a vital gas for sustaining human life and most combustion processes. However, both excessively high and low oxygen...
2026-01-12 -

How Do Nitrogen Oxide Detectors Work?
Against a backdrop of growing global concern over air quality and emissions compliance, the precise monitoring of nitrogen oxides ...
2026-01-09 -

Operating Instructions for Nitrogen Oxide Detectors
Nitrogen oxides (NOₓ, primarily comprising nitrogen monoxide NO and nitrogen dioxide NO₂) are significant atmospheric pollutants...
2026-01-07










 info@eranntexgas.com
info@eranntexgas.com

 13480931872
13480931872