Installation Location of Carbon Monoxide Detectors
Within global industrial safety systems, the installation location of carbon monoxide detectors directly determines their early warning efficacy and accident prevention capabilities. According to statistics from the US National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH), 42% of industrial CO poisoning incidents are directly attributable to improper detector placement. Meanwhile, research by Germany's Federal Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (BAuA) indicates that scientifically positioned detection systems can reduce incident response times by over 60%. Below, Yiyuntian Eranntex provides a systematic analysis of installation strategies for carbon monoxide detectors.
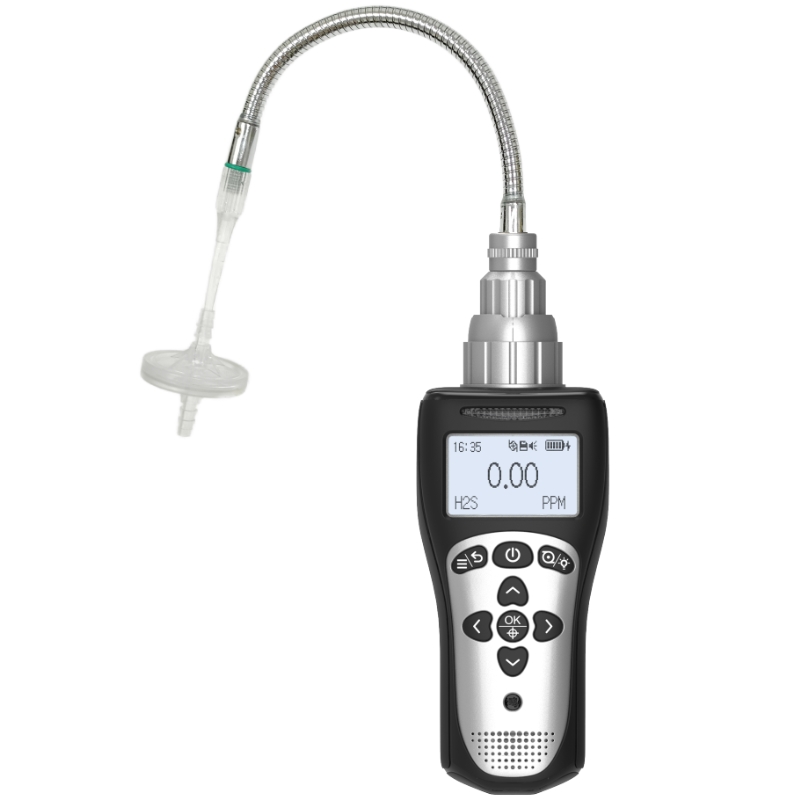
I. Golden Installation Principles for Typical Industrial Scenarios
1. Metallurgical Industry: Precise Monitoring in High-Temperature, High-Dust Environments
In scenarios like steel smelting and non-ferrous metal processing, carbon monoxide primarily originates from blast furnace gas, converter gas, and electric furnace flue gas. The American Iron and Steel Institute (AISI) recommends the “Three-Zone Coverage Method”:
Near the leak source: Install detectors within 1-3 meters of critical points such as blast furnace gas recovery systems and converter secondary dust removal pipelines to capture leak signals immediately. Nippon Steel & Sumitomo Metal Corporation employs a “gradient deployment method” in its electric furnace workshops. By installing detectors at three height levels (1.5m/3m/5m), it achieves three-dimensional monitoring of gases with varying densities, reducing leak response time to under 10 seconds.
Upstream of Personnel Work Zones: Position equipment 5-10 meters upstream of ventilation systems in densely populated areas like steelmaking platforms and continuous casting machine control stations to form a preemptive protective barrier. ThyssenKrupp Steel's implementation demonstrates this layout triggers CO concentration alerts 15 minutes earlier than conventional methods.
Ventilation System Critical Points: Install detectors at the inlets and outlets of ventilation equipment like exhaust fans and air handling units to monitor gas dilution effectiveness in real time. Monitoring data from Alberta oil sands mines in Canada shows that detectors installed at ventilation duct elbows can detect localized concentration exceedances caused by airflow vortices 12 minutes earlier.
Installation Height Specifications: For CO gas with density close to air (molecular weight 28, air average 29), detectors should be mounted 1.5-2 meters above ground level. Tests by the UK Health and Safety Executive (HSE) in steel mills indicate detection sensitivity at this height improves by 40% compared to ground-level installation and by 25% compared to ceiling-mounted installation.
2. Chemical Industry: Explosion-Proof Layout in Flammable/Explosive Environments
In petrochemical, coal chemical, and similar sectors, carbon monoxide often coexists with combustible gases like hydrogen and methane, forming explosive mixtures. The IEC 60079-29-1 standard established by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) explicitly requires:
Explosion-proof zone classification installation: Intrinsically safe (Ex ia) detectors must be used in Zone 0 (continuously explosive gas atmosphere), while flameproof (Ex d) equipment may be used in Zone 1 (potentially explosive gas atmosphere). Saudi Aramco's refinery practices demonstrate that this tiered layout reduces equipment failure rates by 75%.
Pipeline System Monitoring: Install detectors at critical valves and flange connections in process pipelines (e.g., gasification units, ammonia synthesis plants) with intervals not exceeding 15 meters. Case studies by the U.S. Chemical Safety Board (CSB) indicate this layout can detect CO leaks caused by pipeline corrosion 20 minutes earlier.
Tank Farm Protection: Install detectors near breathing valves and safety valves in areas such as liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) storage tanks and methanol storage tanks, and configure them with interlocked emergency shutdown systems. Testing by Equinor (formerly Statoil) demonstrates that this configuration can automatically activate nitrogen purging systems when CO concentrations reach 50 ppm.
II. Customized Solutions for Special Industrial Environments
1. Underground Mines: Airflow Tracking in Confined Spaces
In underground workplaces such as coal mines and metal mines, carbon monoxide primarily originates from blasting operations, internal combustion engine emissions, and coal spontaneous combustion. The Underground Mine Ventilation Code established by the Society for Mining, Metallurgy & Engineering (SME) stipulates:
Return Airway Monitoring: Install detectors every 200 meters in primary return airways, prioritizing the upwind side. Chilean copper mines demonstrate this layout detects CO surges from blasting 30 minutes earlier.
Face Protection: Deploy mobile detectors within 50 meters behind the tunneling head, linked to equipment shutdown mechanisms. Data from Australia's Mining Safety and Health Authority (MSHA) indicates this configuration reduces CO exceedance incidents during tunneling by 83%.
Refuge chamber safeguards: Install dual detectors (one active, one standby) at refuge chamber entrances with audible and visual alarm systems. Verification from Quebec mines in Canada shows this design automatically activates air purification systems when CO concentrations reach 100 ppm.
2. Ship Engine Rooms: Explosion-Proof Monitoring in Confined Spaces
In engine rooms of ocean-going and inland vessels, CO primarily originates from incomplete combustion in diesel generators, boilers, and similar equipment. The International Maritime Organization (IMO)'s SOLAS Convention mandates:
Helical Layout: Detectors should be arranged helically along ventilation ducts at intervals not exceeding 10 meters, with dedicated monitoring points installed at diesel generator exhaust outlets. Verification by Det Norske Veritas (DNV) indicates this layout can increase CO concentration monitoring coverage in engine rooms to 98%.
Dual Redundancy Design: Install two independent detection systems in critical areas like main engine rooms and auxiliary engine rooms, with automatic failover functionality. Testing by Lloyd's Register (LR) shows this design can increase system availability to 99.9%.
Extreme Environment Adaptation: Engine rooms of vessels navigating the Arctic require detectors resistant to low temperatures (-40°C); while vessels operating in tropical regions require high-temperature (70°C) protective devices. Singapore Maritime and Port Authority (MPA) practice demonstrates that this adaptive design reduces equipment failure rates by 60%.
III. Global Industrial Standards and Certification Requirements
Different countries and regions have specific regulations for the installation locations of industrial carbon monoxide detectors:
EU ATEX Certification: Detectors in Zone 0 must obtain Ex ia IIC T6 certification, while those in Zone 1 require Ex d IIC T4 certification. Installation angle deviation must not exceed ±15°.
US NFPA 720 Standard: Industrial detectors must be spaced no more than 15 meters apart, with at least two monitoring points per fire compartment. Alarm thresholds should be set to 50 ppm (sustained for 120 seconds).
Australian AS/NZS 60079.29.2 Standard: Requires detectors in explosive atmospheres to employ explosion-proof designs and maintain stable performance within temperatures of -20°C to +60°C and humidity levels of 0-95% RH.
Scientific installation of industrial carbon monoxide detectors fundamentally establishes a “prevention-monitoring-response” safety loop. By adhering to international standards and implementing specialized layouts tailored to specific scenarios, we can reduce carbon monoxide poisoning risks to manageable levels, building a robust safety defense for industrial production.
Related information
-

How to Calibrate an Oxygen Detectors to Ensure Accuracy?
In fields such as industrial safety, confined space operations, environmental monitoring, and even medical support, the measuremen...
2026-01-14 -

What is the measurement range of an oxygen detectors?
Oxygen detectors are indispensable equipment in industrial safety, environmental monitoring, and confined space operations. Accura...
2026-01-13 -

What is the normal oxygen concentration for an oxygen detectors?
Oxygen (O₂) is a vital gas for sustaining human life and most combustion processes. However, both excessively high and low oxygen...
2026-01-12 -

How Do Nitrogen Oxide Detectors Work?
Against a backdrop of growing global concern over air quality and emissions compliance, the precise monitoring of nitrogen oxides ...
2026-01-09 -

Operating Instructions for Nitrogen Oxide Detectors
Nitrogen oxides (NOₓ, primarily comprising nitrogen monoxide NO and nitrogen dioxide NO₂) are significant atmospheric pollutants...
2026-01-07











 info@eranntexgas.com
info@eranntexgas.com

 13480931872
13480931872