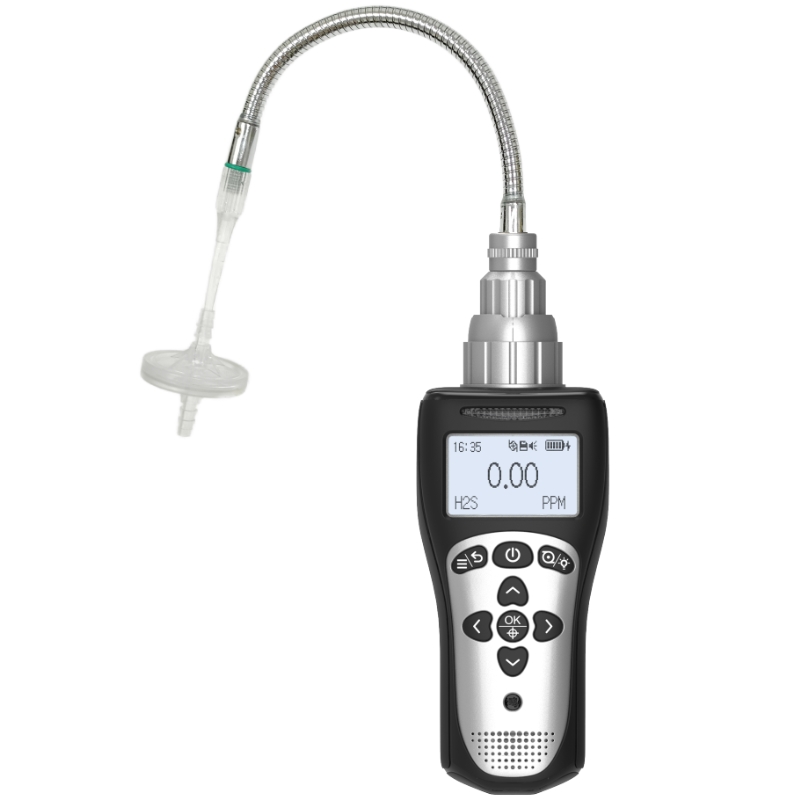
What Can a Four-in-One Detectors Monitor?
In industrial production, construction, firefighting, rescue operations, and numerous other fields, safety remains paramount. As a portable multi-gas detection device, the four-in-one detectors has become a critical tool for safeguarding personnel and preventing accidents through its robust monitoring capabilities. So, what gases does it actually detect? Below, Yiyuntian Eranntex outlines its capabilities.
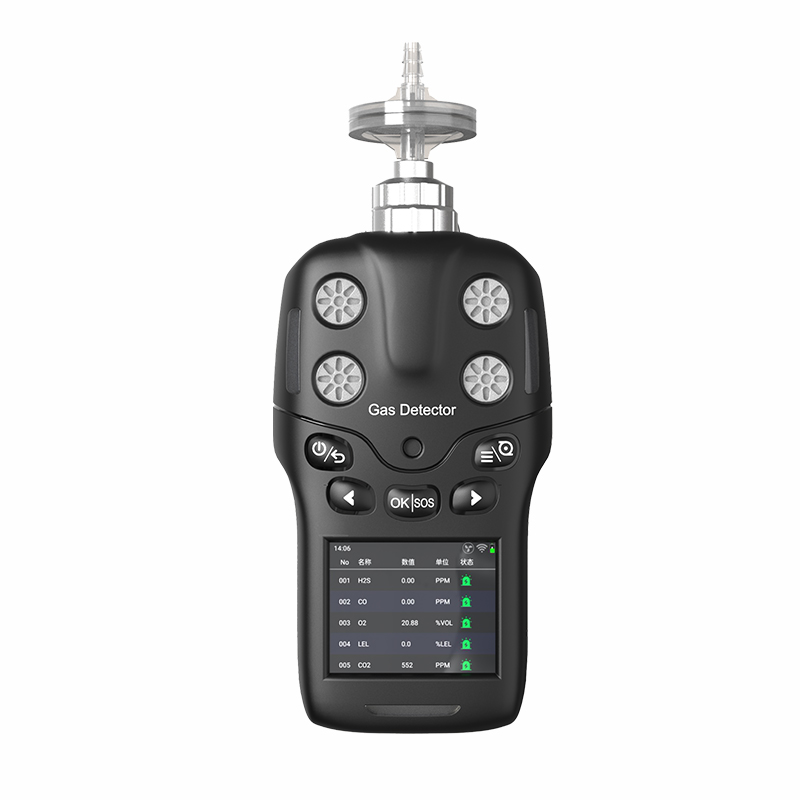

Core Detection Gases: Covering Three Major Safety Risks
The gas detection combination in a four-in-one detectors is not randomly selected but precisely targets three core safety hazards in industrial and daily settings: “explosion risks, oxygen deficiency/asphyxiation, and toxic poisoning.”
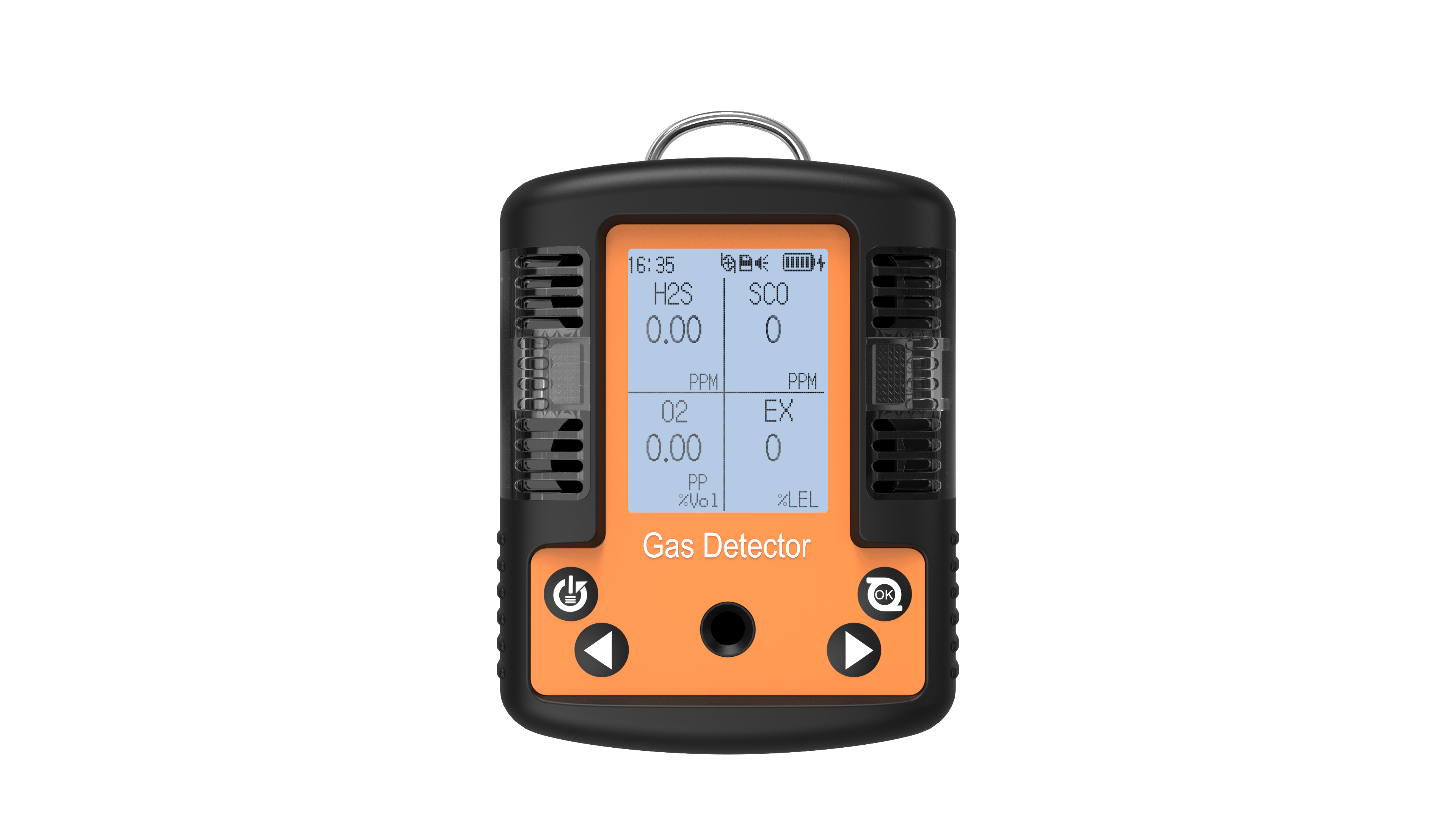
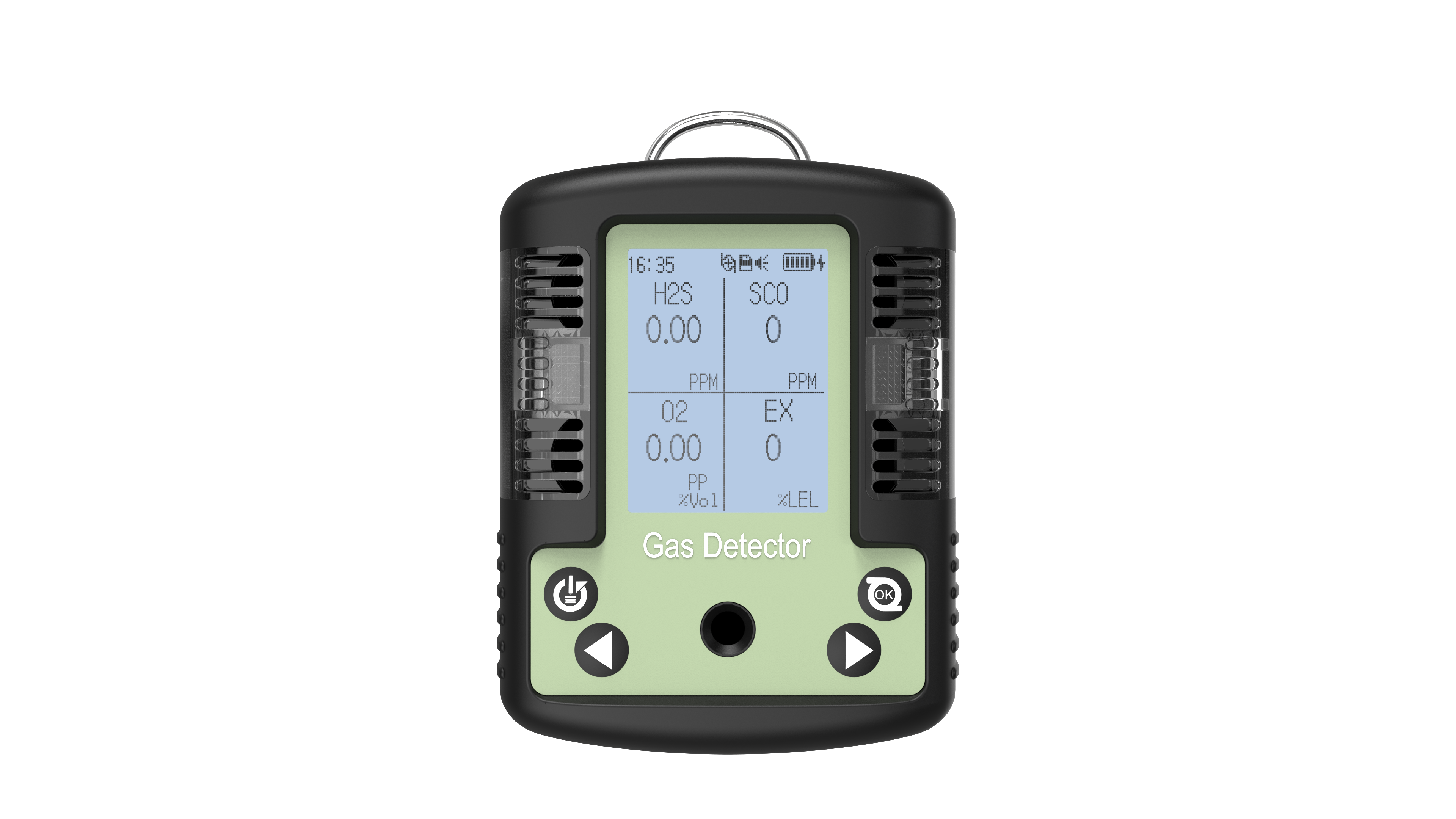
Flammable gases are a primary monitoring target for four-in-one detectors. Gases like methane, propane, and hydrogen can ignite or explode when concentrations in air reach certain levels and encounter open flames or high temperatures. For instance, flammable gas leaks pose constant hazards at gas stations, chemical plant storage areas, and underground coal mines. The four-in-one detectors continuously monitors combustible gas concentrations, typically within a range of 0–100% LEL (Lower Explosive Limit). When concentrations reach the first-level alarm threshold (generally 10% LEL), it indicates gas accumulation requires leak investigation. Upon reaching the second-level alarm threshold (typically 20% LEL), operations must cease immediately, personnel must evacuate, and ventilation must be initiated to effectively prevent explosions.
Monitoring oxygen levels is equally critical. Normal air contains approximately 20.9% Vol oxygen. When oxygen levels drop too low (≤19.5% Vol), individuals may experience symptoms like rapid breathing and dizziness; prolonged exposure can lead to suffocation. Conversely, excessively high oxygen levels (≥23.5% Vol) enhance air's fuel-supporting properties, causing clothing, oils, and other materials to burn intensely upon contact with ignition sources, potentially triggering fires. In oxygen-deficient environments like underground tunnels and sewage wells, as well as oxygen-rich settings such as hospital oxygen chambers and industrial oxygen production facilities, four-in-one detectors accurately measure oxygen levels to ensure workplace safety.
Carbon monoxide and hydrogen sulfide are toxic gases posing severe health hazards. Colorless and odorless, carbon monoxide readily binds with hemoglobin, causing oxygen deprivation in the body. In locations like winter heating boiler rooms, auto repair shops, and underground garages, incomplete fuel combustion may produce carbon monoxide. The four-in-one detectors measures its concentration, typically within a range of 0–1000 ppm. At the Level 1 alarm threshold (50 ppm), exposure for 8 hours may cause dizziness and fatigue. At the Level 2 threshold (100 ppm), exposure for 1 hour can induce nausea and vomiting, requiring immediate evacuation. Hydrogen sulfide is highly toxic; even trace amounts can be fatal. Its detection range is typically 0–100 ppm. At the first-level alarm threshold (10 ppm), a distinct “rotten egg” odor becomes detectable; prolonged exposure irritates the respiratory tract. Reaching the second-level alarm threshold (20 ppm) causes symptoms like eye pain and chest tightness after 10 minutes of exposure, requiring immediate evacuation. In facilities such as refineries and wastewater treatment plants, the four-in-one detectors promptly identifies hydrogen sulfide leaks, safeguarding personnel safety.
Optional Detection Gases: Meeting Diverse Needs
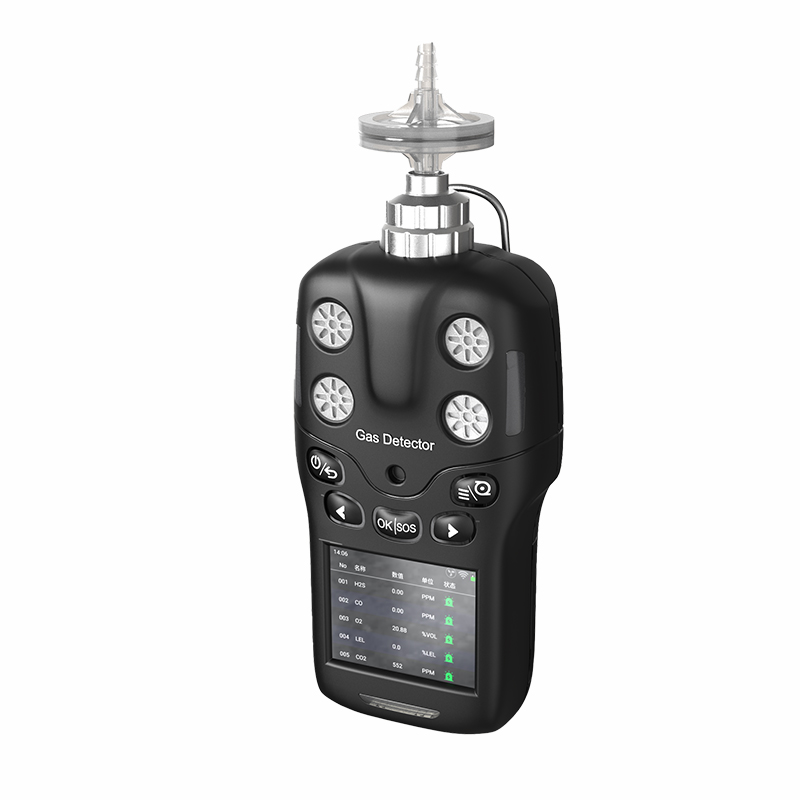
Beyond the four core gases mentioned above, the four-in-one detectors can be customized with additional gas sensors to meet specific site requirements, enabling monitoring of more gases. For instance, in chemical and pharmaceutical industries, monitoring of harmful gases like chlorine, ammonia, and sulfur dioxide may be necessary. In environmental monitoring, detecting gases such as ozone and formaldehyde is also critical. This flexible configuration enables the four-in-one detectors to adapt to complex working environments, providing users with comprehensive safety assurance.
Detection Principle and Advantages: Precise, Reliable, Convenient, and Efficient
The four-in-one detectors operates based on advanced gas sensor technology and electronic principles. It typically houses multiple gas sensors, each employing specific sensing technologies—such as electrochemical sensors for oxygen and toxic gases, and catalytic combustion sensors for combustible gases. When exposed to target gases, the sensors' resistance or electrical signals change. These alterations are converted into digital signals by the detector's internal circuitry and displayed as real-time gas concentration readings on the screen. Should concentrations exceed preset alarm thresholds, the detector immediately triggers audible, visual, and vibrating alarms to prompt personnel to take action.
The four-in-one detectors offers numerous advantages. It is compact and portable, making it easy to carry to various locations; it provides rapid and accurate detection, delivering timely feedback on gas concentration levels; it features audible and visual alarms to ensure personnel can promptly detect hazards; and some high-end models also include data logging and transmission capabilities, facilitating user management and analysis of detection data.
With its robust detection capabilities and multiple advantages, the four-in-one detectors has become an essential tool for ensuring safety across diverse scenarios. Whether in industrial production, construction sites, firefighting operations, or environmental monitoring, it plays a vital role in safeguarding people's lives and health.
Related information
-

How to Calibrate an Oxygen Detectors to Ensure Accuracy?
In fields such as industrial safety, confined space operations, environmental monitoring, and even medical support, the measuremen...
2026-01-14 -

What is the measurement range of an oxygen detectors?
Oxygen detectors are indispensable equipment in industrial safety, environmental monitoring, and confined space operations. Accura...
2026-01-13 -

What is the normal oxygen concentration for an oxygen detectors?
Oxygen (O₂) is a vital gas for sustaining human life and most combustion processes. However, both excessively high and low oxygen...
2026-01-12 -

How Do Nitrogen Oxide Detectors Work?
Against a backdrop of growing global concern over air quality and emissions compliance, the precise monitoring of nitrogen oxides ...
2026-01-09 -

Operating Instructions for Nitrogen Oxide Detectors
Nitrogen oxides (NOₓ, primarily comprising nitrogen monoxide NO and nitrogen dioxide NO₂) are significant atmospheric pollutants...
2026-01-07










 info@eranntexgas.com
info@eranntexgas.com

 13480931872
13480931872