Can Combustible gas detectors detect propane?
Within the global industrial safety and domestic protection sectors, combustible gas detectors have become essential equipment for preventing fire and explosion incidents. For propane—a flammable gas widely utilised in domestic gas supplies, industrial fuels, and chemical raw materials—the ability of detectors to accurately identify its concentration directly impacts the effectiveness of site safety management. Below, Yiyuntian Eranntex's editorial team will analyse the detection capabilities of combustible gas detectors for propane from three dimensions: technical principles, application scenarios, and international standards.

I. Catalytic Combustion Technology: The Core Principle of Propane Detection
The heart of combustible gas detectors lies in sensor technology. For hydrocarbon gases like propane, mainstream devices employ catalytic combustion sensors. Their operation relies on the thermal change generated when gas undergoes flameless combustion on a catalyst surface—propane molecules react with oxygen under platinum wire catalysis, releasing heat that alters the sensor's resistance value. This change is then converted into an electrical signal displaying the concentration level.
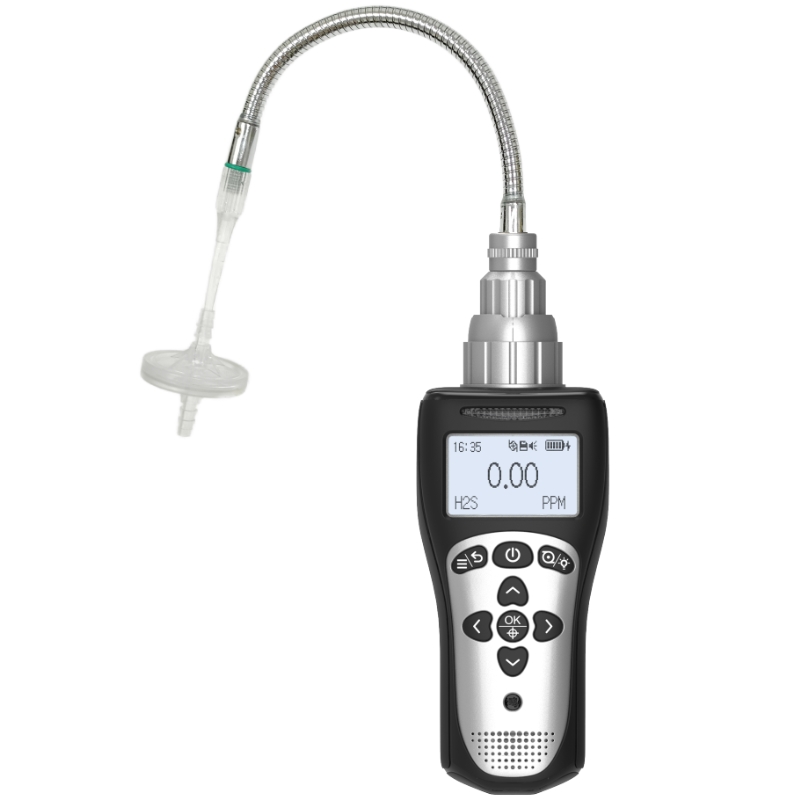
Taking the Sima AM8800L detector as an example, its catalytic combustion sensor detects propane within a range of 0-100% LEL (Lower Explosive Limit), with a response time ≤15 seconds and accuracy maintained within ±5%. Such sensors exhibit exceptional sensitivity to propane, capable of detecting minute leaks as low as 1% LEL, fully meeting international safety standards for early warning equipment.
II. Multi-scenario Coverage: From Domestic Kitchens to Petrochemical Plants
1. Domestic Gas Safety
As the primary component of liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), propane is extensively used in domestic gas cookers, water heaters, and fireplaces across Europe and America. Detectors must be installed 30-60 centimetres above ground level (propane being denser than air), with priority monitoring in kitchens and basement gas cylinder storage areas. For instance, the US National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) mandates that domestic gas systems must incorporate alarms with propane detection capability, with the alarm threshold set at 25% of the lower explosive limit (i.e., 5.25% volume concentration).
2. Industrial and Commercial Applications
In petrochemical plants, propane filling stations, and cold chain logistics centres, fixed detectors connect to central control systems via three-wire systems, continuously monitoring gas concentrations within 12-15 square metre zones. German TÜV certification mandates such equipment operate reliably between -40°C and 65°C with IP65 protection ratings to withstand extreme industrial conditions. For instance, a detection network deployed at a European propane dehydrogenation plant successfully alerted personnel to a 0.8% LEL leak caused by valve deterioration, averting a major incident.
3. Portable Devices: Essential Tools for Emergency Response and Inspection
Portable quad-gas detectors (simultaneously monitoring combustible gases, oxygen, carbon monoxide, and hydrogen sulphide) see widespread application in firefighting, mining, and maritime sectors. Its lithium-ion battery supports 15 hours of continuous operation, while pump-assisted sampling mode enables rapid leak source localisation. The US Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) mandates the use of such devices to verify propane concentrations below the 10% LEL safety threshold prior to confined space entry.
III. International Standards and Certification: Globally Recognised Safety Benchmarks
1. EU EN Standards Framework
The EU EN 50194 standard mandates that combustible gas detectors must obtain CE certification, with propane detection accuracy not exceeding ±10% LEL. Devices must incorporate audible and visual alarms, self-diagnostic fault detection, and data logging capabilities, with a minimum IP54 protection rating. Testing data from TÜV Rheinland laboratories indicates that mainstream detector brands meet response time standards for propane across temperatures ranging from -20°C to 50°C.
2. UL Certification Requirements (United States)
The UL 2075 standard established by Underwriters Laboratories (UL) imposes stricter criteria for domestic propane detectors: alarm volume must be ≥85 decibels, with a false alarm rate below 0.1% per annum. Additionally, devices must pass low-temperature (-25°C) and high-temperature (55°C) cyclic testing to ensure reliability in extreme climates.
3. International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) Specifications
The IEC 60079-29-2 standard establishes globally applicable requirements for gas detectors in explosive atmospheres: propane detectors must have a sensor lifespan of ≥3 years, with calibration intervals not exceeding 6 months. Testing by Riken Keiki Co., Ltd. indicates that sensors utilising nanocatalytic materials can extend propane detection lifespan to 5 years, significantly reducing maintenance costs.
IV. Technological Evolution: From Single Detection to Intelligent Early Warning
With the advancement of IoT technology, new-generation combustible gas detectors now enable cloud-based data management. For instance, Honeywell's Connect series devices transmit real-time propane concentration data to safety platforms via LoRa wireless modules, supporting remote calibration and fault diagnosis. BP's intelligent detection network deployed across its North American refineries employs AI algorithms to analyse historical leak data, elevating propane leak warning accuracy to 99.7%.
Conclusion: Globalised Safety Solutions
From domestic kitchens to multinational petrochemical projects, precise propane detection by combustible gas detectors has become standard practice in global safety management. The internationalisation of technical standards, continuous improvements in sensor performance, and widespread adoption of intelligent warning systems collectively form a comprehensive safety framework covering all operational scenarios. For users, selecting equipment certified to UL, CE, or IEC standards and adhering to regular calibration and correct installation protocols are critical to ensuring propane usage safety.
Related information
-

How to Calibrate an Oxygen Detectors to Ensure Accuracy?
In fields such as industrial safety, confined space operations, environmental monitoring, and even medical support, the measuremen...
2026-01-14 -

What is the measurement range of an oxygen detectors?
Oxygen detectors are indispensable equipment in industrial safety, environmental monitoring, and confined space operations. Accura...
2026-01-13 -

What is the normal oxygen concentration for an oxygen detectors?
Oxygen (O₂) is a vital gas for sustaining human life and most combustion processes. However, both excessively high and low oxygen...
2026-01-12 -

How Do Nitrogen Oxide Detectors Work?
Against a backdrop of growing global concern over air quality and emissions compliance, the precise monitoring of nitrogen oxides ...
2026-01-09 -

Operating Instructions for Nitrogen Oxide Detectors
Nitrogen oxides (NOₓ, primarily comprising nitrogen monoxide NO and nitrogen dioxide NO₂) are significant atmospheric pollutants...
2026-01-07











 info@eranntexgas.com
info@eranntexgas.com

 13480931872
13480931872