What are the different types of Combustible gas detectors?
Within the global industrial safety and civil protection sectors, combustible gas detectors serve as core equipment for preventing explosion incidents. Based on varying technical principles, application scenarios, and detection targets, these devices can be categorised into multiple types. Below, Yiyuntian Eranntex provides an international perspective, analysing mainstream classification methods and their technical characteristics.

I. Classification by Detection Principle: Catalytic Combustion Type and Infrared Optical Type
1. Catalytic Combustion Detectors
Catalytic combustion detectors operate based on the principle of platinum wire resistance variation. When combustible gases (such as propane or methane) enter the detection chamber, they undergo flameless combustion on the platinum wire surface. The resulting heat increases the wire's temperature, altering its resistivity. The instrument calculates gas concentration by monitoring this resistance change, making it suitable for detecting alkane gases in conventional environments.
Technical Advantages:
Low cost, simple maintenance, service life of 3-5 years
Strong resistance to interference, unaffected by humidity or dust
Short response time (<15 seconds), ideal for rapid leak detection
2. Infrared Optical Detectors
Infrared optical detectors utilise the absorption characteristics of gas molecules towards specific infrared wavelengths. By emitting infrared light and analysing reflected intensity changes, they precisely measure concentrations of hydrocarbons such as propane and ethylene.
Technical Advantages:
Strong resistance to poisoning, suitable for environments containing catalytic poisons like silicon and sulphur
Maintenance-free design with sensor lifespans exceeding 5 years
Stable operation in oxygen-deficient environments (e.g., confined spaces)
II. Classification by Application Scenario: Domestic and Industrial Models
1. Domestic Combustible Gas Detectors
Designed for households and small commercial premises, these typically employ semiconductor or catalytic combustion sensors to detect natural gas and liquefied petroleum gas leaks.
Technical Features:
Compact size for straightforward installation (e.g., under kitchen ceilings)
220V mains power supply with audible and visual alarm functions
Detection range: 10-15 square metres; lower sensitivity (>5% LEL alarm threshold)
2. Industrial Combustible Gas Detectors
Industrial detectors feature explosion-proof designs for hazardous environments like petrochemical plants and metallurgy, detecting over 60 industrial gases including propane and hydrogen.
Technical Features:
Die-cast aluminium housing, IP65 protection rating
4-20mA analogue signal + RS-485 digital output
Supports interlocking control with solenoid valves and exhaust fans
Detection range: 25-30 square metres, sensitivity up to 0.5% LEL
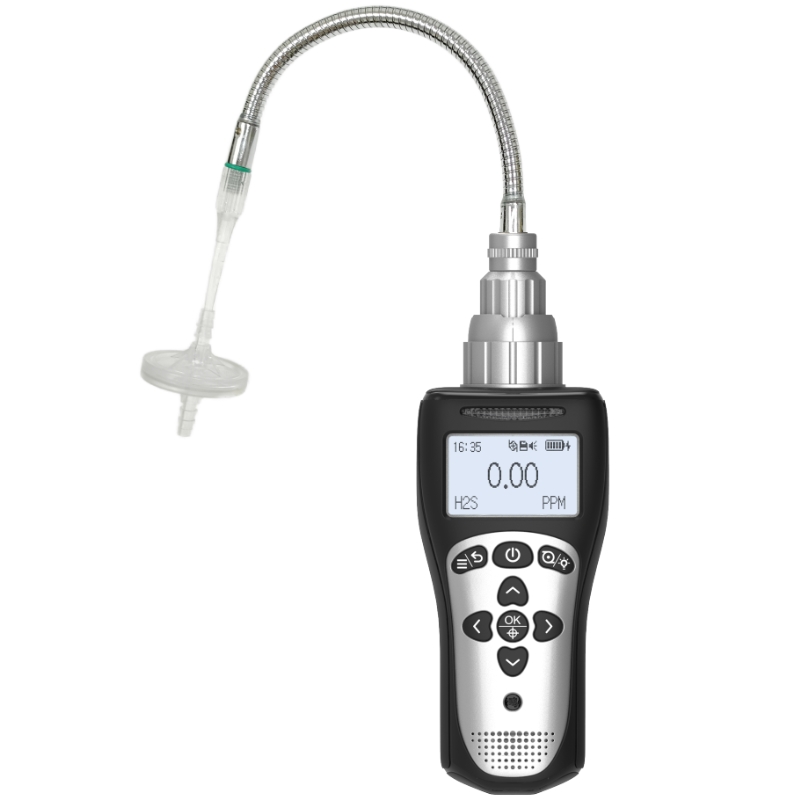
III. Functional Classification: Portable and Multi-Gas Detectors
1. Portable Combustible Gas Detectors
Suitable for on-site inspections and confined space operations, available in diffusion-type and pump-aspiration models.
Technical Features:
Lithium-ion battery power, 12-15 hours continuous operation
Pump-aspiration sampling response time <5 seconds
Data logging capability, stores 100,000 data sets
2. Multi-Gas Detectors
Multi-gas detectors simultaneously monitor combustible gases, toxic gases (e.g., carbon monoxide, hydrogen sulphide), and oxygen concentration, suitable for complex industrial environments.
Technical Features:
Combination of electrochemical sensors and catalytic combustion sensors
Supports simultaneous detection of 1-30 gases
Equipped with GPS positioning and wireless transmission capabilities
From domestic kitchens to multinational petrochemical projects, the technological classification and functional expansion of combustible gas detectors consistently evolve around safety requirements. For users, selecting equipment certified to UL, CE, or IEC standards, alongside adhering to regular calibration and correct installation protocols, remains paramount for ensuring the safe handling of propane and other combustible gases. With the proliferation of intelligent early-warning systems, global industrial safety is advancing towards a more efficient era of proactive protection.
Related information
-

How to Calibrate an Oxygen Detectors to Ensure Accuracy?
In fields such as industrial safety, confined space operations, environmental monitoring, and even medical support, the measuremen...
2026-01-14 -

What is the measurement range of an oxygen detectors?
Oxygen detectors are indispensable equipment in industrial safety, environmental monitoring, and confined space operations. Accura...
2026-01-13 -

What is the normal oxygen concentration for an oxygen detectors?
Oxygen (O₂) is a vital gas for sustaining human life and most combustion processes. However, both excessively high and low oxygen...
2026-01-12 -

How Do Nitrogen Oxide Detectors Work?
Against a backdrop of growing global concern over air quality and emissions compliance, the precise monitoring of nitrogen oxides ...
2026-01-09 -

Operating Instructions for Nitrogen Oxide Detectors
Nitrogen oxides (NOₓ, primarily comprising nitrogen monoxide NO and nitrogen dioxide NO₂) are significant atmospheric pollutants...
2026-01-07










 info@eranntexgas.com
info@eranntexgas.com

 13480931872
13480931872