What is the lifespan of a four-in-one detectors?
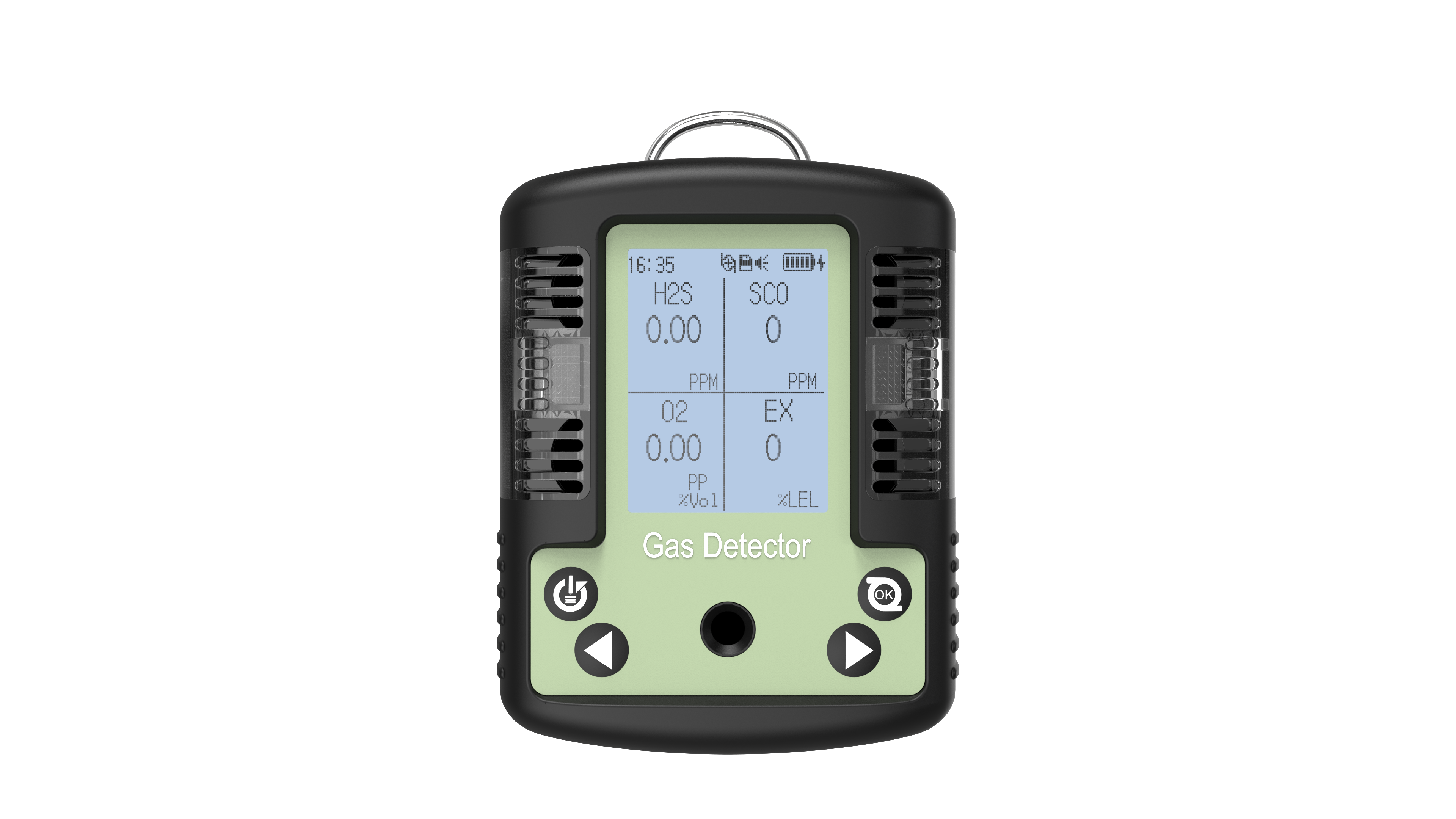
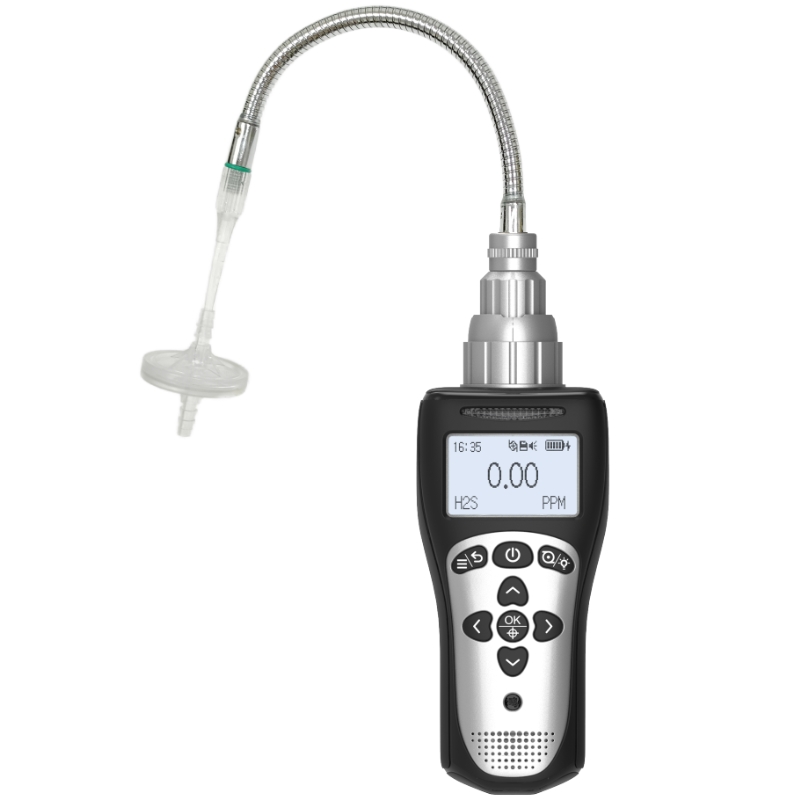
In industrial safety, environmental monitoring, and emergency rescue, four-in-one detectors have become core equipment for ensuring personnel safety. This portable device, capable of simultaneously detecting oxygen, combustible gases, carbon monoxide, and hydrogen sulfide, has a lifespan directly impacting operational safety and data reliability. Below, Yiyuntian Eranntex will systematically analyze the lifespan of a four-in-one detector from three dimensions: technical principles, environmental factors, and maintenance strategies.

I. Core Sensors:
The detection capability of a four-in-one detectors stems from its four built-in gas sensors. Different sensor technologies determine the differences in their basic lifespan:
Electrochemical Sensors (Detecting Carbon Monoxide, Hydrogen Sulfide, and Oxygen):
Based on the principle of an oxidation-reduction reaction between the electrolyte and the target gas, their lifespan is typically 1-3 years. The natural evaporation of the electrolyte means it continues to be consumed even when idle. For example, oxygen sensors often have a shorter lifespan than other electrochemical sensors because the electrolyte dries up faster.
Catalytic Combustion Sensor (Detecting Combustible Gases):
Works by changing the resistance value through heat generated by the oxidation reaction on the catalyst surface. Lifespan is approximately 2-3 years. High concentrations of combustible gases accelerate catalyst aging, leading to decreased detection accuracy.
Infrared Sensor (Detecting Carbon Dioxide, etc.):
Utilizes the principle of non-dispersive infrared absorption, featuring strong anti-interference capabilities and a long lifespan, typically 3-5 years. Its stability makes it the preferred choice for high-precision monitoring applications.
Photoionization Sensor (Detecting Volatile Organic Compounds):
Utilizes the principle of ultraviolet photoionization of gas molecules. Lifespan is approximately 3-5 years, but high humidity environments must be avoided to prevent electrode corrosion.
II. Environmental Factors:
The actual lifespan of the detector is highly dependent on the operating environment:
Extreme Temperature and Humidity:
High temperatures accelerate the internal chemical reaction rate of the sensor, shortening the electrolyte lifespan; low temperatures may reduce sensor sensitivity. High humidity environments easily cause short circuits in circuit boards; for example, equipment operating in Southeast Asian rainforests has a failure rate 40% higher than in normal temperature environments.
Corrosive Gases:
Common gases in chemical industrial parks, such as chlorine and ammonia, can directly corrode sensor electrodes. A case study from a petrochemical company showed that equipment without protective measures developed detection deviations after only 8 months of use in a sulfur-containing environment.
Mechanical Shock:
Frequent drops or vibrations can cause sensor structural displacement. Statistics from the US OSHA show that 15% of detectors are scrapped annually due to physical damage.
III. Maintenance Strategies:
Systematic maintenance can significantly extend equipment lifespan:
Regular Calibration:
It is recommended to perform professional calibration every 3-6 months, using standard gases to verify the sensor response curve. Research by the UK HSE organization confirms that properly calibrated equipment can control the detection error rate within ±3%, while uncalibrated equipment may have an error exceeding 15%.
Cleaning and Maintenance:
After daily operation, wipe the air inlet with a soft cloth to prevent dust blockage. For high-dust environments such as mines, it is recommended to equip the equipment with a dedicated filter. An Australian coal mine extended the average equipment lifespan from 2.1 years to 3.8 years using this measure.
Battery Management:
Lithium batteries should avoid complete discharge; it is recommended to maintain them within the 20%-80% charge range. Norwegian oil company's experience shows that optimizing charging strategies can increase battery cycle life by 60%.
Storage Specifications:
Equipment not in use for extended periods should be placed in a sealed bag and stored in a dry environment at 15-25℃. Tests conducted by a TÜV-certified laboratory in Germany show that properly stored sensors can reduce annual degradation rates to below 0.5%.
IV. Criteria for Determining End-of-Life Status
Equipment should be replaced immediately if the following conditions occur:
Sensor response time exceeds 30 seconds (normally <15 seconds)
Detected values consistently deviate from the standard gas concentration by more than ±10%
Frequent display screen crashes or data jumps
Alarm function failure (e.g., audible and visual alarm volume below 85 decibels)
A multinational energy group's experience on a Gulf of Mexico platform shows that by establishing "sensor health records" and implementing a preventative replacement strategy, the overall lifespan of the equipment can be stabilized at 4.2 years, improving efficiency by 65% compared to a passive maintenance approach.
Conclusion: Scientific Management Creates Safety Value
The lifespan management of a four-in-one detectors is essentially a process of optimizing the return on safety investment. From sensor selection to environmental adaptation, from routine maintenance to end-of-life decisions, every step requires data-driven scientific management. As the International Safety Equipment Association (ISEA) emphasizes, "The value of a detector lies not in its nominal lifespan, but in its ability to continuously provide reliable data throughout each service life." By implementing systematic lifespan management, companies can not only reduce equipment replacement costs but also build a preventative safety culture, constructing the final line of defense for personnel safety.
Related information
-

How to Calibrate an Oxygen Detectors to Ensure Accuracy?
In fields such as industrial safety, confined space operations, environmental monitoring, and even medical support, the measuremen...
2026-01-14 -

What is the measurement range of an oxygen detectors?
Oxygen detectors are indispensable equipment in industrial safety, environmental monitoring, and confined space operations. Accura...
2026-01-13 -

What is the normal oxygen concentration for an oxygen detectors?
Oxygen (O₂) is a vital gas for sustaining human life and most combustion processes. However, both excessively high and low oxygen...
2026-01-12 -

How Do Nitrogen Oxide Detectors Work?
Against a backdrop of growing global concern over air quality and emissions compliance, the precise monitoring of nitrogen oxides ...
2026-01-09 -

Operating Instructions for Nitrogen Oxide Detectors
Nitrogen oxides (NOₓ, primarily comprising nitrogen monoxide NO and nitrogen dioxide NO₂) are significant atmospheric pollutants...
2026-01-07











 info@eranntexgas.com
info@eranntexgas.com

 13480931872
13480931872